|
#5
25th February 2015, 08:27 AM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Kalyani University Chemistry Pass Syllabus
Ok, given below is the syllabus of B.Sc Chemistry of Kalyani University Group A : Atomic structure, periodic properties, nature of chemical bond, principles of chemical analysis ( 50 mark s ) 50 L 1. Atomic structure : 10 L Bohr’s atomic model and its limitations. Idea of de Broglie matter waves, Heisen berg’s uncertainty principle, Schrodinger wave equation, significance of wave function, qu antum numbers, shape of atomic orbitals. Multi electron system : Pauli’s exclusion principle, Hund’s rule of maximum spin multiplicity, stability of half filled and fully filled orbitals, aufbau principle and its limitations, electronic configurations of a toms. 2. Periodic Properties : 5 L Atomic and ionic radii, covalent radii, differe nt electro-negativity scales, ionization energy and their periodic trends. 3. The nature of chemical bond : 20 L Ionic bonding : Size effects, radius ratio rules and their limitations, packing of ions in crystals, hc p and ccp arrangements, lattice energy, Born -Haber cycle and its applications, polarizing power, polarizabil ity, Fajan’s rule. Covalent bonding : Directional characteristics of covalent bond, hybridization and shapes of simple inorganic molecules and ions, valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) Theory. Molecular orbitals of diatomic molecules : LCAO approximation , bonding, antibonding and nonbonding orbitals, MO configurations of simple homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecules, bond properties, bond order and bond strength, resonance and resonance energy, polarity of covalent bonds. Bonding in metals : qualitative idea of free electron and bond theories, conductors, insulators and semiconductors. Hybridisation of C,N,O, formation of σ and π bonds, bond distance, bond angle, bond energy, bond polarity, bond polarisability, steric effect, inductive and field effects, resonance, dipole mo ment, orbital pictures of ethylene and acetylene. Hydrogen bond, dipolar interaction, vander Waals force, physical properties (m.p., b. p., solubility) related to structure 4. Principles of chemical analyses : 15 L i) Qualitative inorganic analyses : Principles and reactions involved in the group separation and identification of cations and anions in the qualitative inorganic analysis. ii) Volumetric analysis: Primary and secondary standard substances/(solutions), principle of acid - base, oxidation reduction and complexo metric titrations, determination of hardness of water; accuracy and precision in quantitative analysis, errors, standard deviation. iii) Theory of acids and bases, strength of acids and bases, P H, hydrolysis of salts, buffer, calculation of PH, solubility and solubility product, common ion effect. Group – B (Organic): Aliphatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives, alcohols and ethers, aldehyde and kelones, organic compounds containing nitrogen, carbohydrates (25) 5. Aliphatic hydrocarbons and their derivatives 7 L Isomerism , synthesis, chemical reactivity of alkanes, mechanism of free radical halogenation of alkanes, sulphonation of alkanes, general method of synthesis of alkenes, chemical reactivity, hydrogenation, electrophilic addition reactions and their mechanism, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, hydration, Markownikoff’s rule, peroxide effect, epoxidation, hydroxylation, ozonolysis, polymerization (only information – no details of reaction mechanism are required). Introduction to general methods of alkyne synthesis, acidity of alkynes, hydration, substitution reaction, polymerization; synthesis and reactivity of alkadiene and alkyl halides. For complete syllabus here is the attachment  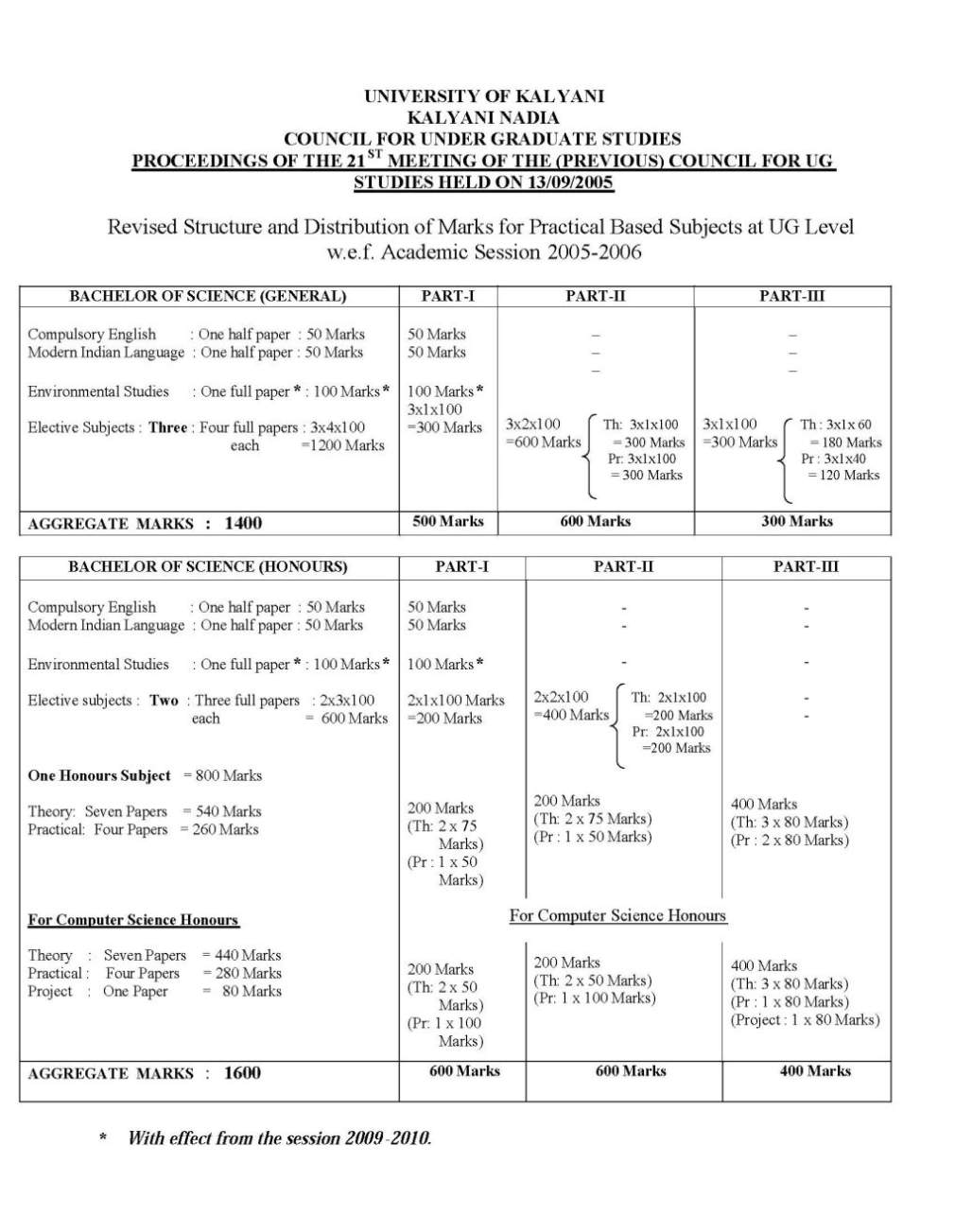     |