|
#2
14th June 2015, 01:29 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Dr MGR University Part Time
As you want I am here giving you syllabus of the part time M.Tech. Industrial Biotechnology course offered by Dr MGR University. Syllabus of the course : Semester 1 : Advanced Microbiology Cell & Molecular Biology Microbial Techniques Lab Bridge Courses (any one will be given) Genetics Basic Principles of Chemical Engineering Mathematics Semester 2 : Quantitative Methods Biochemistry and Enzymology Instrumentation Methods Biochemical Techniques Lab Semester 3 : Genetic Engineering Bioinformatics Genetic Engineering Lab ELECTIVE-I Biology of the Immune System Food Technology Semester 4 : Fermentation Technology Genomics and Proteomics Fermentation Technology Lab ELECTIVE-II Biotechnology of Animal Production Separation Techniques Syllabus of the part time M.Tech. Industrial Biotechnology course  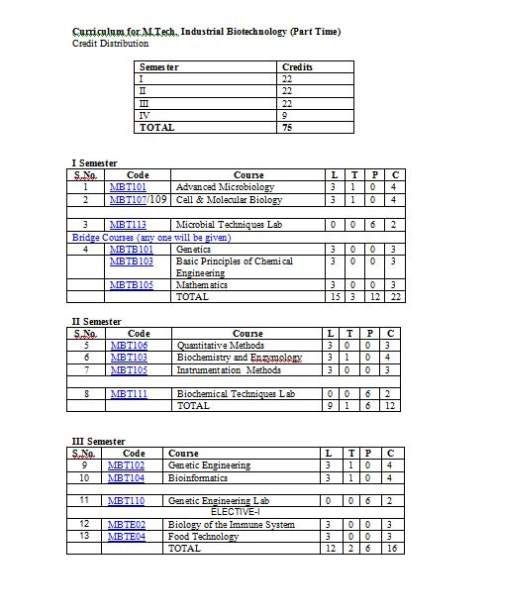 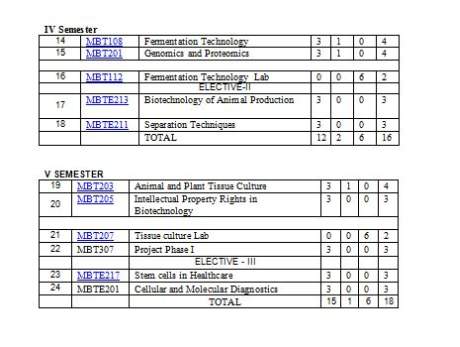 Unit 1: New approaches to Bacterial taxonomy, determination and significance of DNA Base composition, nucleic acid hycridization, RNA fingerprinting, bacterial phylogeny. Unit 2: Metabolic diversity of aerobic heterotrophs – mechanisms in uptake of substrates Entner-Doudoroff pathway, sugar degradation via Pentose Phosphate cycle, methyl glyoxal bypass, diversity in energy metabolism. Unit 3: Bacterial Fermentation – Alcohol fermentation, lactate fermentation, buatyrate & butanol –acetone fermentation, Anaerobic food chains; Chemolithotrophic and phototropic metabolism. Unit 4: Degradation of natural substances – Cellulose degradation, microbial conversion in the rumen, xylan degradation, degradation of starch, fructans, mannan, pectin, agar, chitin, lignin; formation of humus, utilization of hydrocarbons – methane, ethane, propane, butane, aromatic hydrocarbons, xenobiotics. Unit 5: Biodeterioration control and soil, waste and water management – Indicator microorganisms, fouling biofilms, treatment of solid waster, landfills, composting, treatment of liquid waste, biological oxygen demand. References: 1. General Microbiology, Fifth edition, (2006), Stanier RY, Ingraham JL, Wheels ML and RP Painter, Macmillan Press. 2. Bacterial Metabolism, 2nd Edition (1986) Gerhard Gottschalk, Springer Verlag. 3. Microbial Ecology – Fundamentals and Applications, 4th Edition, (2005), Atlas RM and R Bartha. 4. General Microbiology, 7th Edition (1992), Hans G. Schlegel, Cambridge University Press. UNIT 1.INTRODUCTION The cell: A macromolecular assembly, Cellular compartmentization, Organellar architecture. The Nucleus: Chromosomal DNA and its packaging, the global structure of Chromosomes, Chromosome replication, RNA synthesizing and RNA processing, the organization and evolution of the nuclear genome, Cytoskelton. DNAStructure, RNAstructure, organization of the bacterial chromosome, organization of eukaryotic chromosome, UNIT 2.CELL JUNCTIONS AND TRANSPORT SYSTEM: Cell junctions, Cell adhesion, and Extracellular matrix: Cell junctions, Cell – cell adhesion.The plant cell wall. Membrane structure, Transport of molecules and membrane excitability: The lipid bilayer, Membrane proteins, Principles of membrane transport, Ion channels and electrical properties of membranes. The transport of molecules into and out of the Nucleus, The transports of protein into mitochondria, and chloroplasts, Perxisomes, The endoplasmic reticulum, Transport from ER through the Golgi apparatus. UNIT 3.MUTATION, REPAIR AND RECOMBINATION: Chromosome duplication and segregation, Mechanisms of DNA polymerase, types of DNApolymerases, replicon model, eukaryotic replication, role of telomerase.Replication errors and their repair, Mutagens, repair of DNA damage – photoreactivation, base excision repair, homologous recombination, holliday model, recBCD pathway, homologous recombination in eukaryotes, site specific recombination, transposition-transposase – replicative transposition, non-replicative transposition. UNIT 4.TRANSCRIPTION, SPLICING AND TRANSLATION: Types of RNA polymerases, sigma factor, transcription mechanism, rho dependent and independent termination , eukaryotic transcription, RNA processing, RNA polymerase I and III promoter, mechanism of splicing, RNAediting, mRNAtransport, inhibitors of transcription. mechanism of translation, eukaryotic translation factors, peptide bond formation, Wobble hypothesis. Prokaryotes- Lac operon, trp, phage lambda regulation of lytic and lysogenic lifecycle. Eukaryotes – Homeodomain proteins, Zn containing DNA-binding domains, leucind zipper motifs, helix – loop helix proteins, nuceosome modifiers. UNIT 5. CELL SIGNLING AND CELL CYCLE: Cell signaling: general principles of cell signaling, signaling via g- protein linked cell surface receptors, signaling via enzyme linked cell surface receptors,kinase receptors, Cell cycle and division: The general strategy of the cell cycle, The mechanism of cell division, The early embryonic cell cycle, in yeasts and multicellular Animals. Cancer: Cancer as a micro evolutionary process, Tumor cells, Proto – oncogenes and viral oncogenes, Tumor suppressor genes. TEXT / REFERENCE BOOKS 1. Molecular Biology of the Gene, 5th Edition, Watson et al., Pearson Education. 2. Molecular biology by David freifelder 3. Molecular biology- Baltimore 4. Molecular biology- Lodish 5. Molecular biology of cell by Albert et.al. John Wiley & Sons. 6. The Cell by Cooper.ASM Press 7. Cell and Molecular Biology by Karp. John Wiley & sons 1. Sterilization techniques;Cultivation of microorganisms,use of differential and selective media, bacterial growth curve 2. Bacterial staining techniques 3. Biochemical characterization 4. Cultivation and enumeration of bacteriophages 5. Isolation of Antibiotic resistant bacteria 6. Bacterial Conjugation 7. Isolation of a streptomycin resistant mutant 8. Microbial flora of mouth, skin 9. Microbiological analysis of urine and blood specimens 10. Species identification of unknown bacterial cultures Text Book Mixrobiology, Laboratory Manual by Capuccino and Sherman 6th Edition, Pearson Education, (2006) Unit I Introduction Nature of genetic material, Mendelian laws of inheritance, law of segregation and laws of independent assortment. Dominance and lethal genes-Dominance relationships, lethal gene action, gene interactions and Epistasis –Types of gene interaction and molecular basis of gene interaction. Unit II Chromosome structure and organization.Chromosome morphology, composition of chromatin,Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic organization, heterochromatin. Different types of (polytene and lamp brush chromosome, giant chromosomes) Chromosomes. Human Chromosomes and Functions. Unit III Sex chromosomes and inherited diseases.Vehicles of heredity, sex determination in plants and animals, Autosomal dominant disorders sex linked inheritance, non-disjunction of X chromosomes, linkage and crossing over, interference, coincidence.molecular diseases Hemoglobinopathies, disorders of coagulation, colour blindness, hemophilia. Multiple alleles ABO blood groups, Rh group system Unit IV Gene Transfer & Mapping. Mapping techniques-calculation of large map distances, mapping genes by mitotic segregation and recombination, mapping by insitu hybridization. Gene transfer in bacteria-transformation, transduction, conjugation and their mapping Unit V Population Genetics.Principles of Hardy Weinberg law-Gene frequency, genotype frequency,Hardy Weinberg equilibrium and application, factors affecting gene frequencies. Polymorphism and characteristic features, inbreeding. Text Books: Genetics By Monroe W Stricberger Principles of Genetics By Gardner Fundamentals of Genetics By B.D.Singh References: Genetics By Goodenough Genes and Genomes By Singer and P.Berg Genetics By Griffith UNIT I Stoichiometry & chemical equations. Units, dimensions & conversions. Phase rule, Henry’s law, Raoult’s law & their applications to different systems .Material balance for non-reacting & reacting systems, recycle & bypass. UNIT II Properties of fluids & fluid statistics. Fluid statistics, laminar & turbulent flows, velocity distribution in pipes, pressure drop in pipes & fittings.Stokes law & its applications, orifice & venturi meter. Pumps & their characteristics. UNIT III Steady state conduction: Fourier’s law, concept of resistance to heat transfer, conduction with heat generation.Convection, Heat transfer in laminar turbulent flows. Heat exchanger: Sizing of shell & tube heat exchangers. Heat transfer in agitated vessels. Boiling & condensation. UNIT IV Fundamentals of mass transfer: molecular diffusion in fluids & solids, concept of mass transfer coefficient. Equilibrium stage, absorption, UNIT V Fundamentals of Chemical reaction engineering: Equilibrium criteria for homogeneous chemical reactions. Text / Reference books: 1. Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering, Mc Cabe, W.L.Smith, J.C and Harriot P., McGraw Hill International Edition, Fifth Edition 2. Basic Principles of Calculation in Chemical Engineering, Himmelblau D.M, Sixth Edition 3. Levenspiel.O, “Chemical Reaction Engineering “, JohnWiley, Second Edition, 1972.2 Here is the attachment. |