|
#4
23rd March 2015, 09:19 AM
| |||
| |||
| Re: CET Physics Karnataka
Here I am providing you Syllabus and Previous Years Question Papers of Physics for Karnataka CET (Common Entrance Test) for you preparation. Karnataka CET Physics Syllabus: 1. WAVES AND SOUND Waves: formation of waves, types of waves, wave amplitude, frequency, wave length and velocity - relation n =f l - equation for progressive wave, intensity, super position of waves. Problems Sound: Properties, velocity in gases, Newton - Laplace formula, factors affecting velocity - intensity and loudness, units, Noise and Music beats as an example of superposition of waves, Doppler effect, formula for general case, discussion for individual cases. Problems Stationary waves: Modes of vibration in pipes, laws of vibration of stretched strings, sonometer, Problems. Ultrasonics: Production (mention of methods), properties and applications Acoustics of buildings: reverberation, Sabine's formula (mention), requisites for good acoustics and methods of achieving them. 2. PHYSICAL OPTICS Introduction to theories of light Interference of light: Coherent sources, Young's double slit experiment, expression for path difference, conditions for constructive and destructive interference, width of interference fringes. Problems Diffraction of light: Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction, Fraunhofer diffraction through a single slit (qualitative explanation), limit of resolution, Rayleigh's criterion, resolving powers of telescopes and microscope. Problems Polarisation of light: transverse nature of light waves, methods of producing plane polarized light, Brewster's law, double refraction, dichroism, polariods and their applications, optical activity and specific rotation. Problems. 3. ELECTROSTATICS Electric charge: Coulomb's law, dielectric constant, SI unit of charge, electric intensity and potential, relation connecting them, derivation of expression for potential at a point due to an isolated charge. Gauss theorem and applications, intensity at a point (a) due to a charged spherical conductor (b) near the surface of a charged conductor, Problems Capacitors: parallel plate, spherical, cylindrical, expressions for the capacitances, principle of a capacitor, effect of dielectric, energy stored in a capacitor, combination of capacitors, uses, Problems 4. CURRENT ELECTRICITY Different effects of electric current: potential difference, resistance, colour code, Ohm's law and its limitations, variation of resistance of a conductor with length- area of cross section and temperature, resistivity, superconductivity, thermistor and its applications, combination of resistors, EMF of a cell, current in a circuit, branch currents, grouping of cells, expression for different cases, potentiometer, problems Kirchhoff's laws: Condition for balance of a Wheatstone's bridge, metre bridge, Problems Magetic effect of current: direction of field, right hand clasp rule and magnitude - Laplace's law, force on a charged particle moving across a magnetic field (qualitative), magnetic field strength, flux density, magnetic flux density at a point on the axis of (a) a circular coil carrying current (derivation), (b) a solenoid carrying current (without derivation), tangent law, tangent galvanometer (with theory), Problems Force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field: Fleming's left hand rule, force between two parallel conductors carrying current, definition of ampere, suspended coil galvanometer (with theory), conversion of galvanometer into ammeter and voltmeter, Problems Magnetic materials: Intensity of Magnetising field (H), intensity of magnetisation (I) and magnetic induction (B) - relation connecting them, permeability and susceptibility, properties of dia, para and ferromagnetic substances, hysteresis cycle and its significance, retentivity and coercivity, uses of magnetic materials. Electromagnetic induction: Laws, self and mutual induction, induction coil (principle), principle and working of a generator, expression for sinusoidal emf, peak, mean and rms values, impedance, current in R, L & C and RLC circuits, power factor, choke and transformer (principle), principles of a ac meters (moving iron and hot wire types) Problems. 5. MODERN PHYSICS Introduction to modern physics: types of spectra, E. M. spectrum, types of electron emission. Quantum theory of radiation: Explanation and applications of photoelectric effect, atom models, Bohr's theory of hydrogen atom, derivation of expressions for orbital radius, orbital velocity, energy of electron and wave number, spectral series, energy level diagram, de Broglie matter waves, Problems. Nuclear Physics: Nuclear size, charge, mass and density, constituents, amu in terms of electron volts, magnetic moment and nuclear forces, mass defect and binding energy, nuclear fission, chain reaction, critical size, nuclear reactor, nuclear fusion, stellar energy, radiation hazards, Problems. Radioactivity: Properties of radioactive radiations, decay law, decay constant, Soddy's group displacement law, half life and mean life, expression for half life, radio isotopes and their uses, Problems. Solid state electronics: Band theory of solids (qualitative), classification into conductors, insulators and semi conductors, p-type and n-type semi conductors, characteristics of p-n junction, rectifying action of diode, half wave and full wave rectifiers. Transistors, pnp and npn, characteristics, relation between alph and beta transistors as an amplifier (qualitative -npn in CE mode) Previous Years Question Papers of Physics for Karnataka CET: Karnataka CET Physics Paper 1 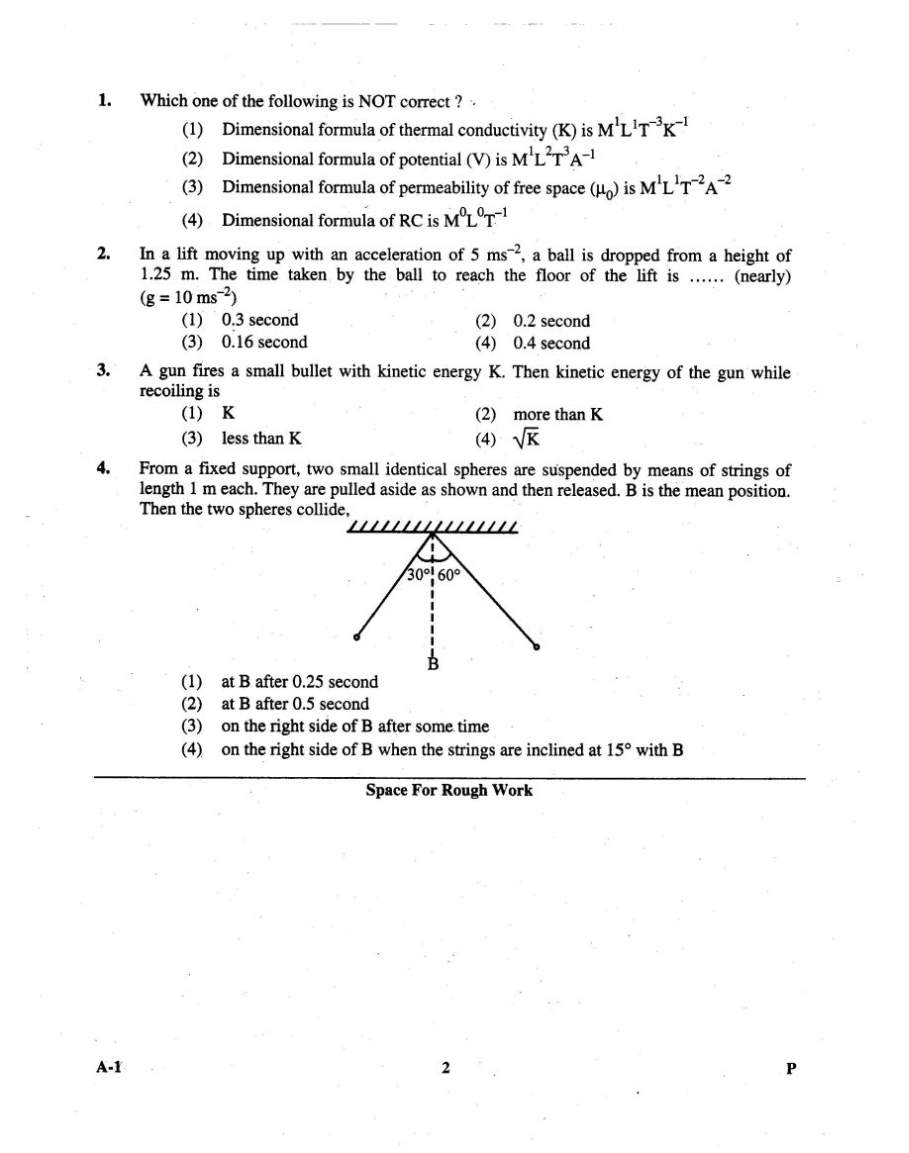   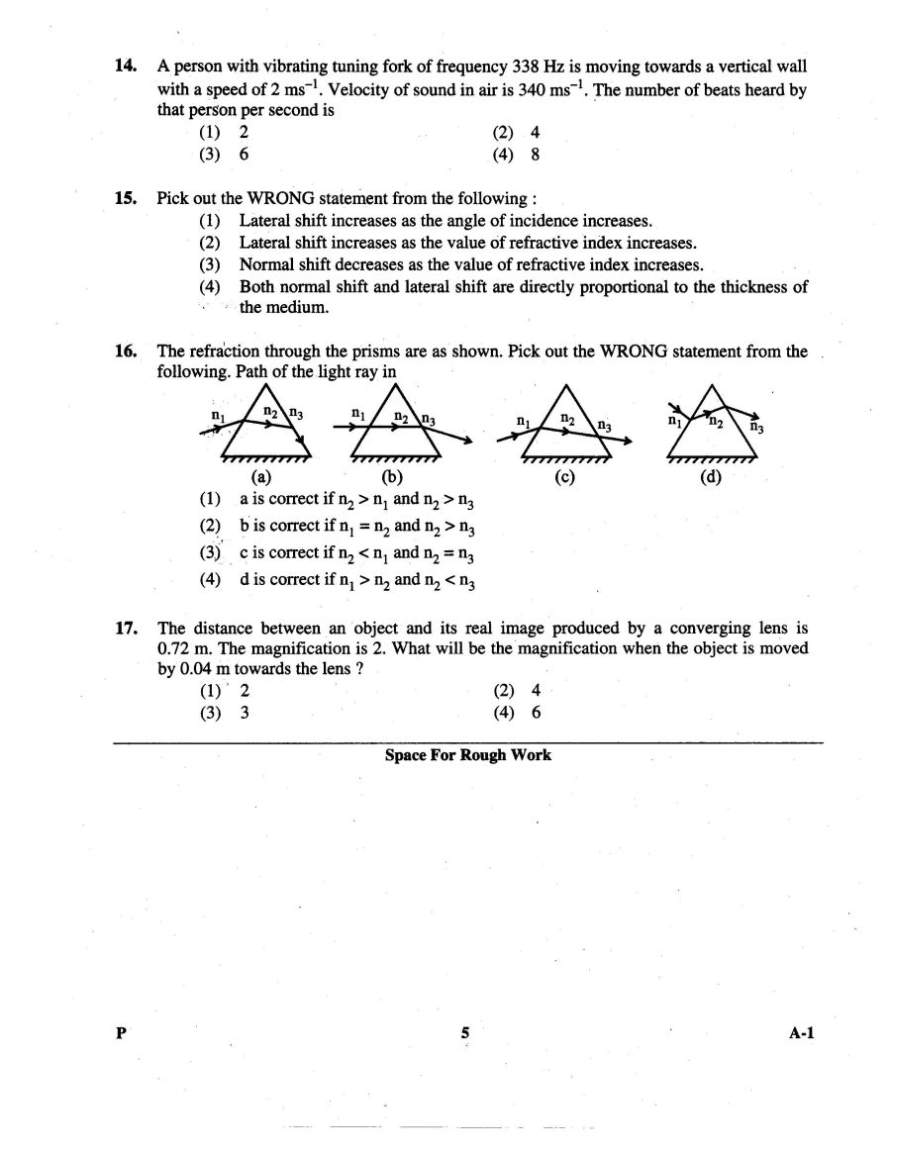   |