|
#4
14th May 2020, 08:22 AM
| |||
| |||
| Re: EEE Paper RTU
The Syllabus for B. Tech (Electrical & Electronics Engineering), 3rd semester offered by RTU (Rajasthan Technical University) on which the question paper is based is as follows: 3EX1A: ELECTRONIC DEVICES & CIRCUITS (Common to EE, EX, EC and EI) 1 Semiconductor Physics: Mobility and conductivity, charge densities in a semiconductor, Fermi Dirac distribution, Fermi-Dirac statistics and Boltzmann approximation to the Fermi-Dirac statistics, carrier concentrations and Fermi levels in semiconductor. Generation and recombination of charges, diffusion and continuity equation, transport equations, Mass action Law, Hall effect. 2 Junction Diodes: Formation of homogenous and hetrojunction diodes and their energy band diagrams, calculation of contact potential and depletion width, V-I characteristics, Small signal models of diode, Diode as a circuit element, diode parameters and load line concept, C-V characteristics and dopant profile. Applications of diodes in rectifier, clipping, clamping circuits and voltage multipliers Transient behavior of PN diode Breakdown diodes, Schottky diodes, and Zener diode as voltage regulator Construction, characteristics and operating principle of UJT 3 Transistors: Characteristics, Current Components, Current Gains: alpha and beta. Variation of transistor parameter with temperature and current level, Operating point, Hybrid model, DC model of transistor, h-parameter equivalent circuits.CE, CB and CC configuration DC and AC analysis of single stage CE, CC (Emitter follower) and CB amplifiers AC & DC load line, Ebers-Moll model Biasing & stabilization techniques Thermal runaway, Thermal stability 4 JFET & MOSFET: Construction and operation of JFET & MOSFET, noise performances of FET, parasitic of MOSFET, small signal models of JFET & MOSFET. Biasing of JFET's & MOSFET’s Low frequency single stage CS and CD (source follower) JFET amplifiers.FET as voltage variable resistor and active load 5 Small Signal Amplifiers at Low Frequency: Analysis of BJT and FET multistage amplifier, DC and RC coupled amplifiers. Frequency response of single and multistage amplifier, mid-band gain, gains at low and high frequency. Analysis of DC and differential amplifiers, Miller's Theorem, use of Miller and bootstrap configuration Cascade and cascade configuration of multistage amplifiers (CE-CE, CE-CB, CS-CS and CS-CD), Darlington pair Syllabus B. Tech (EEE), 3rd semester Rajasthan Technical University 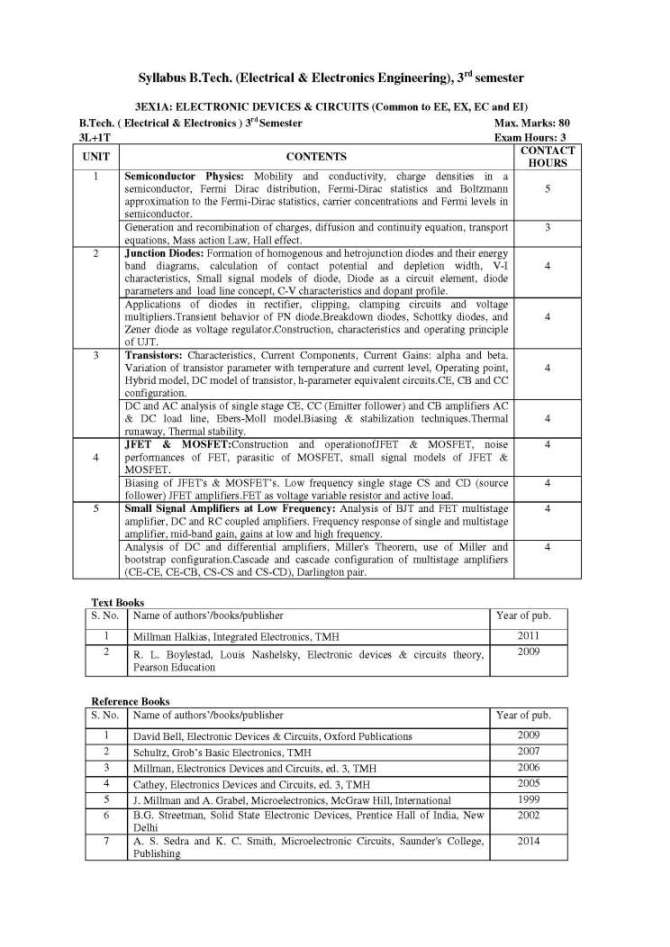 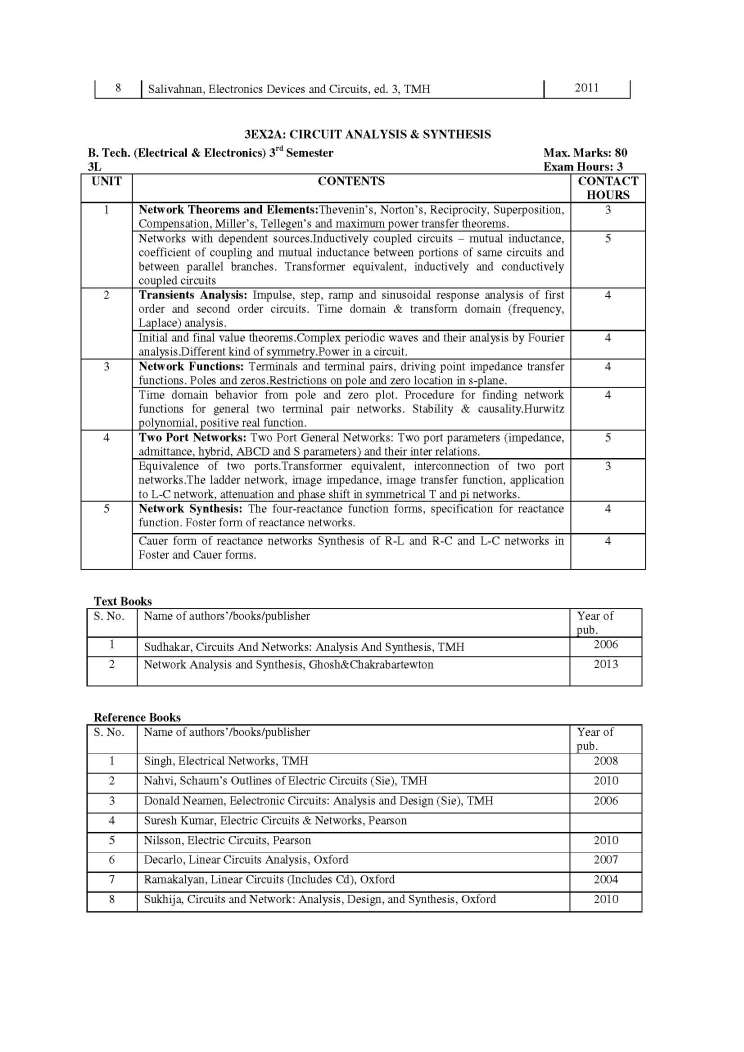 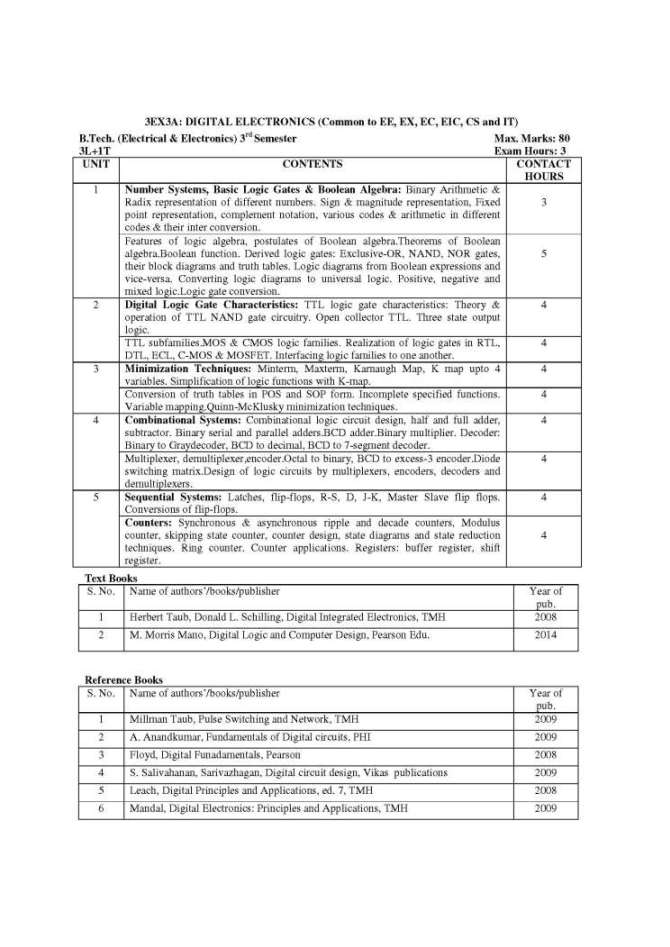 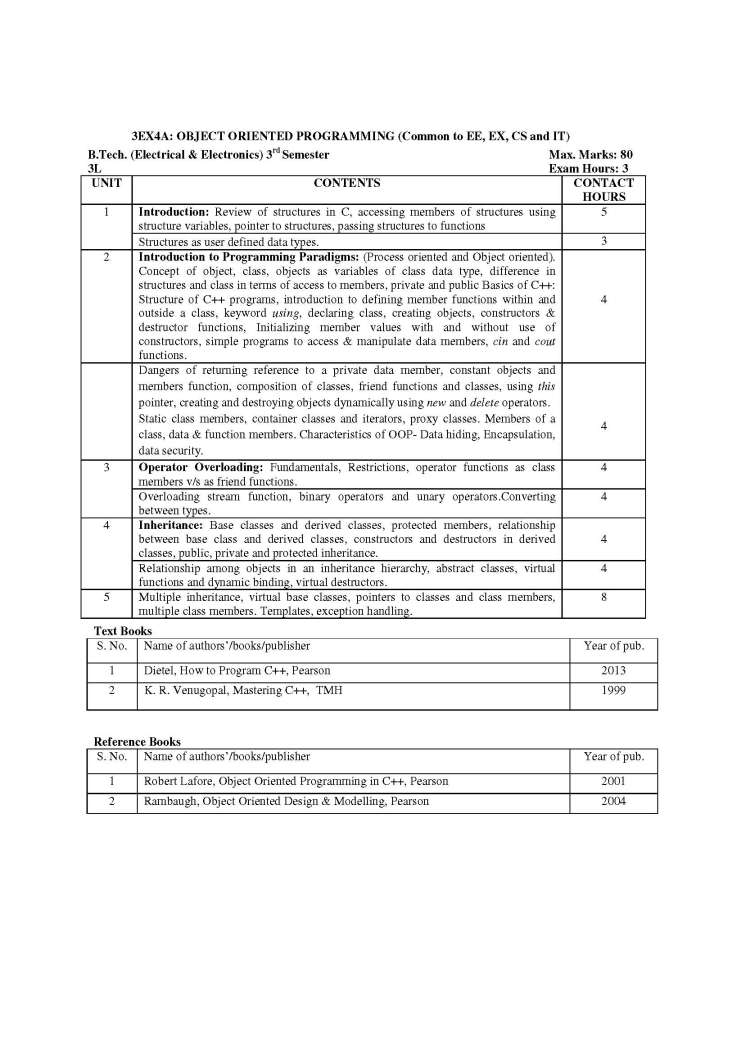 |