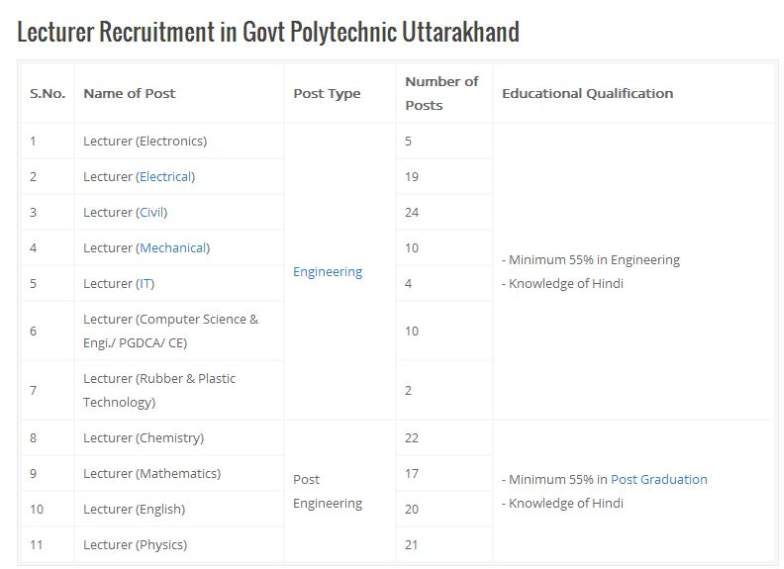
| Re: Uttarakhand Polytechnic Lecturer Recruitment
Hello brother as you ask for the Syllabus of Uttarakhand Polytechnic Lecturer Recruitment on your demand I am providing it to you
Section 1
General Studies
1. Current events of National and International importance.
2. Sports and Entertainment.
3. Indian History (ancient, medieval, modern).
4. Indian National Movement.
5. Geography of India and World, Economy and Agriculture.
6. Natural Resources, Planning, Sustainable and Inclusive Development.
7. Natural Calamities and Disaster Management.
8. Human Resource Development Index in India.
9. Basic Knowledge of Indian Constitution – Salient features of Indian Constitution, Fundamental Rights and Duties, Directive Principles of State Policy. The Union Executive – The President, Prime Minister, Council of Ministers, The Union Legislature – Parliament, The Judiciary – Supreme Court and High Court, State Government and Administration – Governor, Chief Minister and Council of Ministers, Legislative Assembly, Panchayati Raj Institutions.
10. Human Rights – Meaning of Human Rights, Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948), Human Rights and Duties in India, National Human Rights Commission.
11. Various aspects of Rural and Urban Development.
12. General Science- application of Science in day- to – day life.
13. Development and Environmental Problems- Main Problems related to development, population growth, environmental pollution, emission of greenhouse gases and measures to overcome the problems. Laws for environmental conservation.
14. Biotechnology and Health Issues: Biotechnology, development of vaccines against new diseases, genetically developed plants, regeneration of worn out and dead tissues and human organs, control of pollution using bacteria, biofuel.
15. Development of Science and Technology In India :
A. Energy and Water Resources: Energy crisis, energy conservation, conventional energy sources, renewable energy, types of Indian water resources, use and management.
B. Information, Communication Technology and Computers: Development of information and communication technology in India, benefits and adverse effects. Basic components and structure of computer and its uses.
16. Modern Indian Education System-Indian Education Commission, University Grants Commission, National Policy on Education, Education for Equality, Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, Use of Modern Technology in Education.
17. National Knowledge Commission – Main Recommendations- Right to Education, e-Governance.
18. Teaching Competence and Communication-Teaching Skills, Teaching Methods and Techniques, Teaching Aids Comprehensive and Continuous evaluation.
19. Value based Education-Types of Values, Development of Values through Education.
Section 2
Knowledge of Uttarakhand State
1. General Geography- Location and Extent, Structure and Relief, Climate and Drainage systems, Demography, Transport and Communication network.
2. History-
(a) Ancient Period- Inhabiting races and tribal groups, Dynasties (Kuninda, Paurav and Katyuri).
(b) Medieval Period – Later Katyuri, Chand and Panwar dynasties.
(c) Modern Period- Gorkha and British Period, Post-Independence scenario.
3. Natural and Economic Resources- Water, Forest, Minerals, Livestock, Agriculture and Horticulture, Wild-life conservation, Parks and Sanctuaries
4. Political and Administrative Setup- Administrative setup atthe State, District and Tehsil levels.
5. Education and Culture- Educational and Training Institutions, Dialects and Languages, Customs and Traditions, Festivals, and Fairs.
6. Social Reform Movements – Coolie Begar, Dola -palki, and Forest Movements.
7. Economic Development- Hydro-electricity, Industry, Horticulture, Tourism, and Herbal Industry development.
8. Developmental Plans– Scheduled Castes and Tribal Development planning.
9. Important Contemporary events.
10. Sports and Entertainment.
Section 3
General Intelligence Test
Questions of verbal, non-verbal and analytical types, analogies, syllogism, similarities, differences, missing numbers, characters and sequences, space visualization, problem solving, analysis, decision making, visual memory, discrimination, observation, relationship concepts, direction sense, coding – decoding, arithmetical reasoning, verbal and figure classification, data representation and analysis, arithmetical number series. The test would also include questions designed to test the candidates’ ability to deal with abstract ideas, facts and figures, symbols and their relationships, arithmetical and numerical computations and other analytical, mathematical and quantitative functions.
Section 4
सामान्य हिंदी
1. पर्यायवाची शब्द
2. विलोम शब्द
3. शब्द-समूहों के लिए एक शब्द
4.उपसर्ग/ प्रत्यय
5. तत्सम-तद्भव शब्द
6. वर्तनी-शुद्धि
7. वाक्य-शुद्धि
8. समास
9. संधि-विच्छेद
10. मुहावरे एवं लोकोक्तियाँ
Section 5
General English
1. Use of Prepositions.
2. One Word substitution.
3. Use of Articles in English.
4. Common errors in English.
5. Idioms.
6. Conversion of one part of speech into another, e.g., Noun to Adjective, and the like.
7. Comprehension of a given passage in English (questions will be asked on the following topics).
A- Synonyms.
B- Antonyms.
C- Hindi translation of a given underlined English Sentence.
D- One more question will be also based on the comprehensive passage.
Questions of verbal, non-verbal and analytical types, analogies, syllogism, similarities, differences, missing numbers, characters and sequences, space visualization, problem solving, analysis, decision making, visual memory, discrimination, observation, relationship concepts, direction sense, coding – decoding, arithmetical reasoning, verbal and figure classification, data representation and analysis, arithmetical number series. The test would also include questions designed to test the candidates’ ability to deal with abstract ideas, facts and figures, symbols and their relationships, arithmetical and numerical computations and other analytical, mathematical and quantitative functions.
|