|
#2
3rd November 2015, 05:00 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Rayat Bahra University Punjab
Candidates possessing B.Tech in (ME) or AMIE (Associate Member of Institute of Engineers) with minimum 50% aggregate marks in qualifying examination are eligibile to apply for M.Tech (ME) course in University School of Engineering &Technology of Rayat Bahra University in Punjab. Study Scheme or Syllabus Semester: I Name of the Subject Optimization Techniques Heat and Mass Transfer Non-traditional Machining Processes Advanced Design of Machine Elements Finite Element Method Finite Element Method Lab. Semester II Research Methodology Control Theory Production and Operations Management Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing Lab. Elective – 1 Soft Skills Elective -1 (offered in M.Tech. 2nd Sem.) Product Design and Development Material Science and Technology Strategic Entrepreneurship Semester III Industrial and Production Management Elective -2 Dissertation Preli. Elective - 2 (offered in M.Tech. 3rd Sem.) ME7302 ME7303 ME7304 Semester IV Dissertation Study Scheme or Syllabus M Tech ME 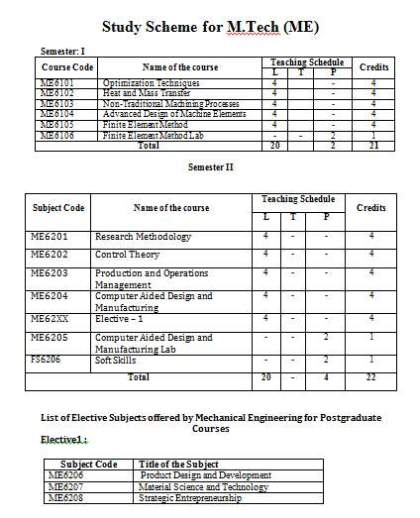 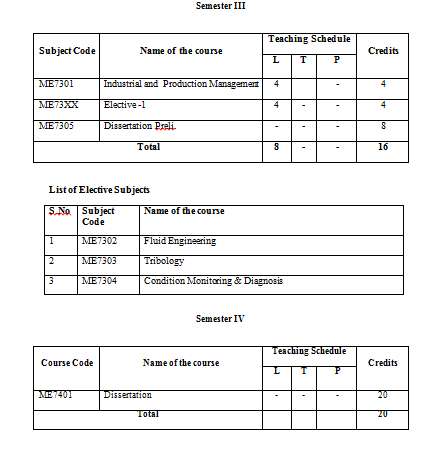 UNIT I (6 Hours) Introduction to Operations Research: Meaning of Operations Research, Modeling in operation research, principles of modeling, Introduction to linear and non-linear programming problems and formulation of problems. UNIT II (8 Hours) Linear programming: Problem formulation, graphical solution, simplex method, big M method, two phase method, dual simplex method, duality theory, sensitivity analysis. UNIT III (5 Hours) Network Models: Transportation problem, Transshipment problem, Assignment problem, Traveling-salesman problem, Shortest route problem, Minimal spanning tree problem, Maximum flow problem. UNIT IV (8 Hours) CPM & PERT: Characteristics & uses, drawing of network, removal of redundancy in network. Computation of EOT, LOT, free slack, total slack in CPM and PERT, crashing, resource allocation. UNIT V (6 Hours) Dynamic Programming: Deterministic and Probabilistic Dynamic programming. UNIT VI (4 Hours) Simulation Models: Generation of Random number. Use of Coeff. random numbers for system simulation. Use of computers for system simulation. UNIT VII Non-linear Programming: Characteristics, Concepts of convexity, maxima and minima of functions of n variables using Lagrange multipliers and Kuhn-Tukker conditions, Quadratic programming , One dimensional search methods, Fibonacci and golden section method, Optimization using gradient methods for unconstrained problems. Learning Outcome At the end of this course students should be able to formulate the models and analyze them using various optimization techniques. UNIT I (6 Hours) Basic Concepts: Mechanism of Heat Transfer – Conduction, Convection and Radiation– Fourier Law of Conduction UNIT II (10 Hours) Conduction: General Heat Conduction Differential Equation in Rectilinear, Cylindrical and Spherical Co-Ordinates, One Dimensional Steady State Heat Conduction – Conduction through Plane Wall, Cylinders and Spherical systems – Composite Systems – Conduction with Internal Heat Generation – Extended Surfaces, Straight Fins of Rectangular, Triangular and Trapezoidal Sections, Effectiveness Of Fins. Two-Dimensional Steady State Conduction: Semi Infinite and Finite Flat Plate, Temperature Field .In Infinite And Finite Cylinders, Conduction Through Spherical Shell, Graphical Methods, Unsteady State Conduction. UNIT III (10 Hours) Convection: Review Of Continuity And Momentum, Heat Transfer Coefficients – Boundary Layer Concept – Types of Convection – Forced Convection – Dimensional Analysis, Differential Equations For Incompressible Fluids, External Flow – Flow over Plates, Cylinders and Spheres – Internal Flow – Laminar and Turbulent Flow – Combined Laminar and Turbulent Flow, Wall Temperature And With Constant Heat Flux, Forced External Flow Over Flat Plate, The Two Dimensional Velocity And Temperature Boundary Layer Equations, The Karman-Pohlhanton Approximate Integral Method. UNIT IV (10 Hours) Radiation: Radiation Through Non-Absorbing Media, Hottels Method Of Successive Reflection, Review Of Methods Of Analogous, Electrical Circuits, Radiation Through Absorbing Media, Logarithmic Decrement Of Radiation, Gas Radiation, Apparent Absorptivities Of Simple Shaped Gas Bodies, Net Heat Exchange Between Surfaces Separated By An Absorbing Gas, Radiation of Luminous Gas Flames. UNIT V (9 Hours) Mass Transfer: Basic Concepts – Diffusion Mass Transfer – Fick’s Law of Diffusion – Steady state, Molecular Diffusion – Convective Mass Transfer – Momentum, Heat and Mass Transfer Analogy – Convective Mass Transfer Correlations. |