|
#2
29th October 2014, 03:47 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Question Paper Class 12th CBSE
Below I am listing some of the questions from the question paper only and for detailed question paper I am attaching a PDF file which you can download for free: Emulsion : These are liquid - liquid colloidal system dispersion of finially divided droplets in another liquid if a mixture of two immiscible or partially miscible liquids is shaken a coarse dispersion of one liquid in the other, is obtained which is called emulsion. Types two types (a) oil dispersed in water (o/w) e.g. milk (b) water dispersed in oil (w/o) e.g. cod liver oil (i) Dr. Satpal : He is benevolent person. NHRC suggested to the government to provide medical care, financial assistance setting up of supper speciality hospitals for treatement and prevention of the deadly diseases in the affected villages all over India. (ii) Morphine (iii) Saccharin Chemisorption increases with increases of temperature since it required activation energy. Reactivity of the Zn is greater than Ag therefore it displace Ag from its salt solution therefore we can get pure Ag. 2[Ag(CN)2]–+Zn (s) [Zn (CN)4]–2 + 2Ag (s) Kohlrausch law : According to this law limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte. e.g. limiting molarconductivity of NaCl is - ºm(NaCl) + – Conductivity : Always decreases with decrease in concentration both, fer weak and strong electrolyte since the number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution. Principle : By the using of electrolytic refining we can obtained pure metal from crude metal in this method pure metal act as a cathode and crude metal act as a anode. e.g. In the refining of Cu : Pure Cu rod act as a cathode Crude Cu rod act as a anode CuSO4(aq) act as a electrolyte reaction : at anode : Cu(s) Cu+2 (aq) + 2e– at cathode Cu2+ (aq) + 2e– Cu(s) (i) P4 + H2O : Reaction is not possible in ordinary conditions however in different specific condition gives different product. (ii) XeF4 + O2F2 XeF6 + O2 Question Paper Class 12th CBSE 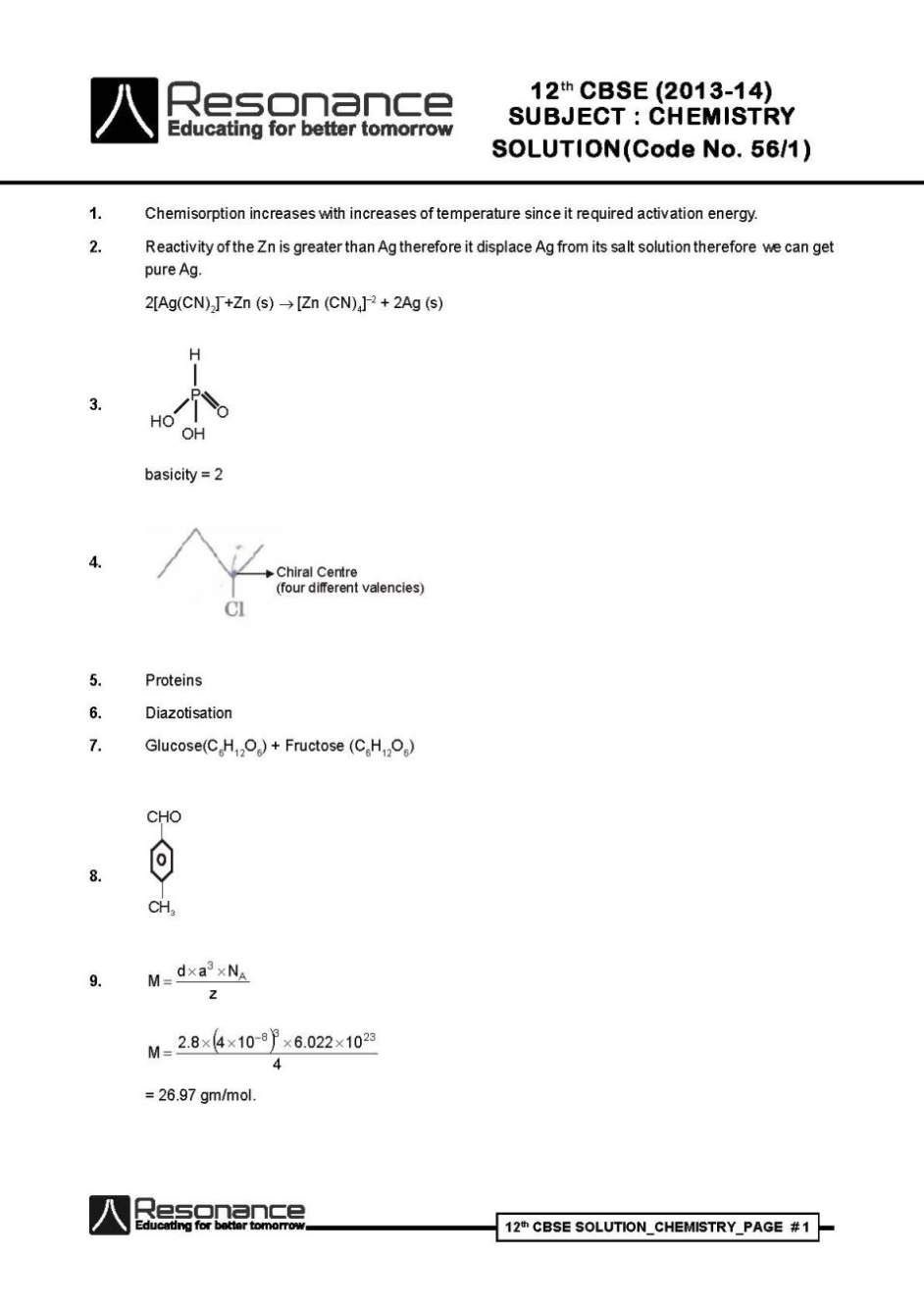    |