| 9th September 2019 04:21 PM | |
| sumit | Re: MDU Rohtak MA Geography Syllabus As you are asking for MDU Rohtak MA Geography program Syllabus , so on your demand I am providing same here : 16GEO021C1 GEOMORPHOLOGY Credit: 04 (3+1+0) End Semester Exam : 80 marks Internal Assessment : 20 marks Total : 100 marks Time : 3 hrs. Learning Objectives: The objectives of this course are to introduce the concepts in Geomorphology in adequate manner, many facets of surface relief features and to understand various aspects of their growth and evolution on the Earth. Learning Outcomes: The course will provide an understanding of the conceptual and dynamic aspects of landform development. Students will also learn the relevance of applied aspects of Geomorphology in various fields. Unit-1 Geomorphology - Definition, Nature and scope, History and development of geomorphic ideas : Fundamental concepts - uniformitarianism, geological structure, process and stage. The Earths interior - structure and constitution, Recent Views. Plate tectonics- meaning and concept; plates, plate margins and boundaries; plate motion; Tectonic activities along the boundaries and Distribution of plates. Unit-II Endogenetic processes - Faulting, folding and their geomorphic expressions. earthquake concept, causes, classification, intensity and magnitude, Geographical distribution. Vulcanism - concept, mechanism and causes; Volcanoes- classification, volcanic materials; Topography associated with vulcanicity and geographical distribution. Unit-III Exogenetic processes : Weathering and mass wasting - meaning and concept, controlling factors, classification and significance. Dynamics of fluvial, aeolian, glacial and karst processes and resulting landforms. Unit-IV Applied Geomorphology - meaning; Applications of Geomorphology in Regional planning, engineering projects, mineral exploration and hydrology. Regional Geomorphology of Punjab plain, Aravalli Region and Thar desert of India. 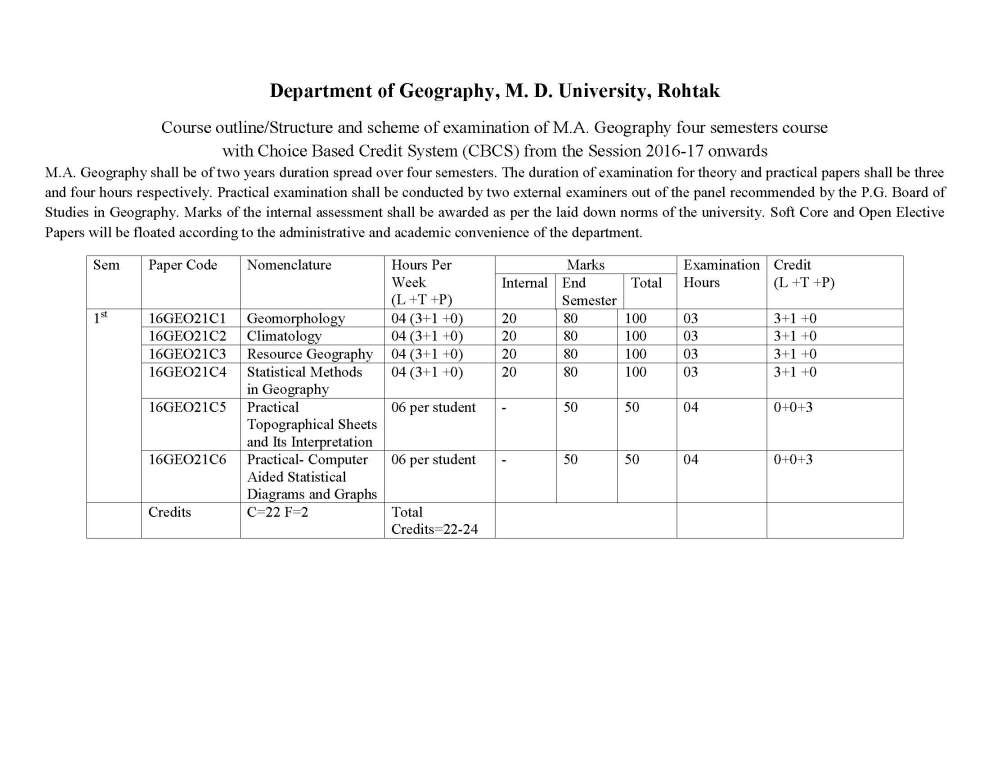 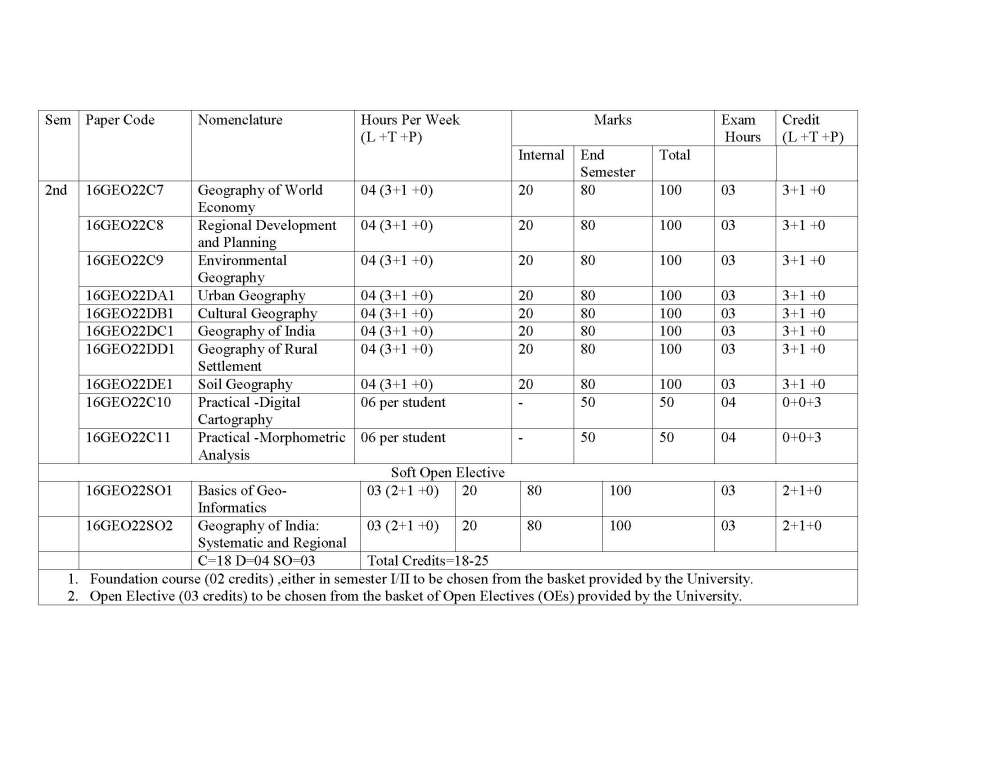 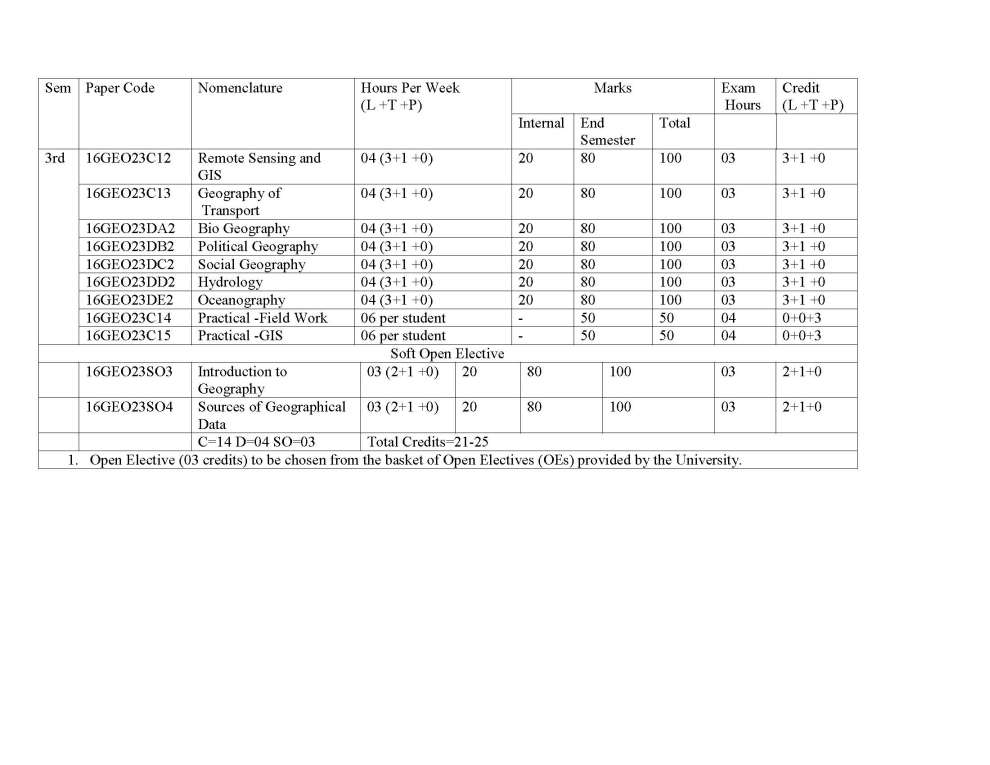 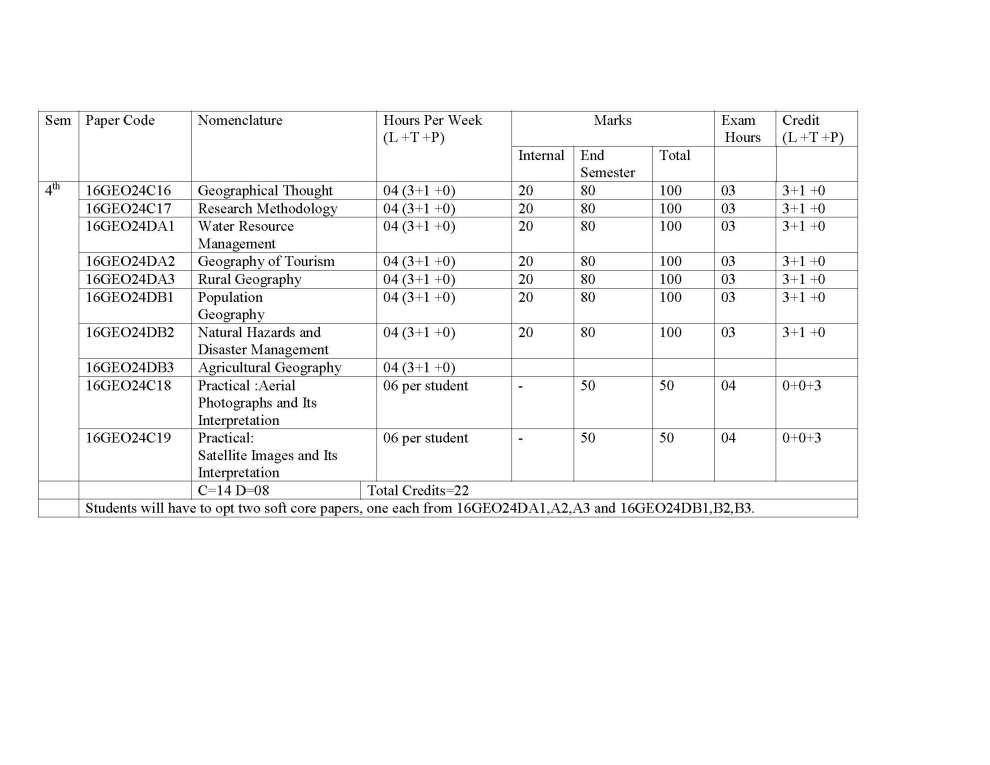 |
| 9th September 2019 04:19 PM | |
| Unregistered | Re: MDU Rohtak MA Geography Syllabus Hi buddy here I have come to collect MDU Rohtak MA Geography program Syllabus so that I could start my exam preparation so will you plz let me know from where I can collect it ?? |
| 7th June 2015 01:57 PM | |
| Arun Vats | Re: MDU Rohtak MA Geography Syllabus As you want I am here providing you syllabus of the MA Geography course offered by the MDU Rohtak. Syllabus : Semester 1 : Geomorphology Climatology Resource Geography Any one of the following: i) Population Geography ii)Urban Geography iii)Geography of Rural Settlements iv) Cultural Geography Practical :Interpretation of Topographical Sheets and computer Aided Statistical Diagrams Semester 2 : Geography of India: Contemporary Issues Geography of Transport Statistical Methods in Geography Any one of the following: (i) Agricultural Geography (ii) Political Geography (iii) Social Geography (iv) Geography of Health Practical : Field work and Report Writing. Semester 3 : Geography of World Economy Oceanography Environmental Geography Any one of the following (i) Geography of Tourism (ii) Hydrology (iii) Biogeography (iv) Soil Geography Practicals: Morphometric Analysis M.A. Geography : Semester-I Paper-I Geomorphology End Semester Exam : 80 marks Internal Assessment : 20 marks Total : 100 marks Time : 3 hrs. UNIT-I Geomorphology - Definition, Nature and scope, History and development of geomorphic ideas : Fundamental concepts - uniformitarianism, geological structure, process and stage. The Earth’s interior - structure and constitution, Recent Views. Plate tectonicsmeaning and concept; plates, plate margins and boundaries; plate motion; Tectonic activities along the boundaries and Distribution of plates. UNIT-II Endogenetic processes - Faulting, folding and their geomorphic expressions. earthquake concept, causes, classification, intensity and magnitude, Geographical distribution. Vulcanism - concept, mechanism and causes; Volcanoes- classification, volcanic materials; Topography associated with vulcanicity and geographical distribution. UNIT-III Exogenetic : Weathering and mass wasting - meaning and concept, controlling factors, classification and significance. Dynamics of fluvial, aeolian, glacial and karst processes and resulting landforms. UNIT-IV Applied Geomorphology - meaning; Applications of Geomorphology in Regional planning, engineering projects, mineral exploration and hydrology. Regional Geomorphology of Punjab plain, Aravalli Region and Thar desert of India. Note : The question paper will have five units. Each of the first four units of question paper will contain two questions from each unit of the syllabus. Candidate(s) are required to attempt one question from each unit. The unit five shall be compulsory and shall contain eight short answer type questions covering entire. All questions carry equal marks. Recommended Readings : 1. Bloom, A.L. (1992) Geomorphology, Second Edition, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi. 2. Dayal, P. (1990) A Text Book of Geomorphology, Shukla Book Depot, Patna. 3. Husain Majid (2002), Fundamentals of Physical Geography, Second Edition, Rawat Publications, Jaipur and New Delhi. 4. Singh Savindra (1993), Physical Geography, Prayag Pustak Bhawan, Allahabad. 5. ____________(1998), Geomorphology, Prayag Pustak Bhawan, Allahabad. 6. Strahler, A.N. and Strahler, A.H.(1996), Introducing Physical Geography, John Willey and Sons, New York. 7. Strahler, A .N. (1988), Earth Sciences, Harper and Row Publishers, N.D. 8. Thornbury, W.D. (1991), Principles of Geomorphology, John Wiley, New Delhi (Indian reprint) 9. Wooldridge, S. W and Morgan, R.S. (1991), An Outline of Geomorphology, Orient Longmans,Calcutta. M.A. Geography: Semester I Paper-II Climatology End Semester Exam : 80 marks Internal Assessment : 20 marks Total : 100 marks Time : 3 hrs. UNIT-I Nature and Scope of Climatology Climatic elements – atmospheric temperature, pressure, moisture , general atmospheric circulations jet stream. UNIT-II Weather system and disturbances - airmass, fronts, Cyclones, Tornades, ; Ocean atmospheric interaction- EI Nino, Monsoon winds. UNIT-III Global climate system - Approaches to climatic classification ;Classification of Koppen, and ThornthwaiteMajor climate of the world-tropical and polar. UNIT-IV Climatic changes - evidences, possible causes, global warming acid rain and problems of acid rain. Note : The question paper will have five units. Each of the first four units of question paper will contain two questions from each unit of the syllabus. Candidate(s) are required to attempt one question from each unit. The unit five shall be compulsory and shall contain eight short answer type questions covering entire syllabus. All questions carry equal marks. Recommended Readings : 1. Aggarwal, S.K. (1972), Fundaments of Ecology,Ashish Publishers, New Delhi. 2. Barry, R.G. and Chorely, R.J., Atmosphere, Weatherand Climate, ELBS, Methuen & Co. Ltd. London. 3. BhutaniSmita, (2000) Our Atmosphere, KalyanaiPublishers, New Delhi. 4. Critchfield, H.J. (1987) Climatology, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi. 5. Griffith, J.F. and Driscell, D.M. (1982) Survey of Climatology, Charles Merril. 6. Lal, D.S. (1993) Climatology, Chaitanya Publishing House, Allahabad. 7. Riehl, H. (1968), Introduction to Atmosphere, McGraw Hill, New York. 8. Robinson,P.J. and Henderson Sellers (1986) Contemporary Climatology, Longman, London. 9. Trewartha, G.T. (Latest edition) Introduction to Climate McGraw Hill, New York. M.A. Geography: Semester-I Paper-III: Resource Geography End Semester Exam : 80 marks Internal Assessment : 20 marks Total : 100 marks Time : 3 hrs. UNIT-I Nature, scope and significance of the Geography of Resource, Definition and concept of Resources, Classification of Resources. UNIT-II Models of Natural Resources Process: Zimmermann’s Primitive and Advance Models of natural resource process, Kirk’s Decision Model, Brookfield System Model. UNIT-III Use and Misuse of Resources: Soil Resource, Water Resource, Forest Resource and Mineral Resources, Future prospects of Natural resources UNIT-IV Conservation and Management of Natural Resources: Meaning and Concept of conservation of Natural Resources, Resources Conservation and Management Methods of Natural resources: Soil Resource, Water Resource, Forest Resource and Mineral Resources, Problems of Natural Resource Management in India. Note: The question paper will have five units. Each of the first four units of question paper will contain two questions from each unit of the syllabus. Candidate(s) are required to attempt one question from each unit. The unit five shall be compulsory and shall contain eight short answer type questions covering entire Syllabus. All questions carry equal marks. Recommended Readings: 1. Borton, I. and R.W. Kates. (1984) Readings in Resource Management and Conservation, University of Chicago Press, Chicago. 2. Bruce,Mitchell (1989) Geography and Resource Analysis, John Wiley and Son, New York. 3. Eliot Hurst, M.E. (1972) A Geography of Economic Behaviour : An Introduction, Duxbury Press, California. 4. Guha, J.L. and P.R.Chattroj (1994) Economic geography- AStudy of Resources, The World Press Pvt. Ltd. Calcutta 5. Martino, R.L. (1969) Resource Management. Mc Graw Hill Book Co., London. 6. Negi, B.S.(2000) Geography of Resources, Kedar Nath and Ram Nath,Meerut 7. Owen, Oliver, S.(1971) Natural Resource Conservation : A Ecological Approach. Mc Million New Delhi. 8. Raja, M. (1989) Renewable Resources, Development, Concept Pub. New Delhi. 9. Ramesh, A.(1984) Resource Geography (Ed.) R.P. Misra, Contribution to Indian geography, Vol Heritage Publishers, New Delhi. 10. Singh, A and Raja, M. (1982) Geography of Resources and conservation (Hindi Edition) Pargati Parkashan, Meerut. 11. Zimmermann, E. W. (1951) World Resources and Industries, Harper and Brothers, New Delhi. M.A. Geography: Semester-I Paper-IV (i): Population Geography End Semester Exam : 80 marks Internal Assessment : 20 marks Total : 100 marks Time : 3 hrs. UNIT-I Population Geography: Definition, nature and scope; relationship with other disciplines – demography and population studies; sources of data with particular reference to India – census, vital or civil registration system, Sample Registration System, Sample surveys with particular reference to NSSO and NFHS; Problems of their reliability and comparability. UNIT-II Population Distribution and Growth: Factors affecting population distribution; Population growth - trends and determinants; spatial dimension of population growth in India; Theories of population growth – pre-Malthusian views, Malthus’ Theory, views of socialist writers, optimum population theory, demographic transition model. UNIT-III Components of population change: trends and patterns in fertility and mortality levels; Theories of fertility; Migration: major international migrations; features of internal migration in India; theories of migration; population composition and characteristics - age and sex composition, literacy, marital status and economic characteristics of population. UNIT-IV Population and development: population growth and economic development; population growth and environmental quality; population control movement: population policies and its types; India’s Population Policy: Post independence development – Reproductive and Child Health Programme. . Note : The question paper will have five units. Each of the first four units of question paper will contain two questions from each unit of the syllabus. Candidate(s) are required to attempt one question from each unit. The unit five shall be compulsory and shall contain eight short answer type questions covering entire syllabus. All questions carry equal marks. Recommended Readings: Beaujen- Garnier J (1966) Geography of Population; Longman, London. Bhende Asha A and Kanitkar (2002) Principles of Population Studies, 14th Edition, Himalaya Publishing House, Mumbai. Chandana, R.C. (2002) Geography of Population : Concepts, determination and patterns, Kalyani Publishers, New Delhi. Clarke, J.I. (1992) Population Geography, Second Edition, Pergamon Press, Oxford England. Hassan, M.I. (2005) Population Geography, Rawat Publication, Jaipur. Premi, M.K. (1991) India’s Population Heading Towards a Billion, B.R. Publishing Coporation, New Delhi. M.A Geography: Semester-I Paper IV (ii): Urban Geography End Semester Exam : 80 marks Internal Assessment : 20 marks Total : 100 marks Time : 3 hrs. Unit –I Definition, nature and scope of urban geography; different approaches and recent trends in urban geography; Origin and evolution of urban places in Ancient, Medieval, Modern and Post-Modern periods- factors, stages, evolution and characteristics. Unit-II Aspects of urban places: Location, site and situation - definition, nature and significance; Urban ecological processes; Theories of city structure-concentric zone theory, sector theory, multiple nuclei theory and social area analysis. Unit-III Settlement systems: the rank-size distribution of cities, Primate city distribution, central place theory of Christaller and Losch; the rural-urban fringe-definition, delimitation and structure; city-region relationship. Unit-IV Urbanization: definition and measures of urbanization, factors affecting urbanization, cycle of urbanisation; Historical development of urbanization in the world: Primordial and definitive urbanization; Regional aspects of world urbanization; Patterns and trends of urbanisation in India. Note : The question paper will have five units. Each of the first four units of question paper will contain two questions from each unit of the syllabus. Candidate(s) are required to attempt one question from each unit. The unit five shall be compulsory and shall contain eight short answer type questions covering entire syllabus. All questions carry equal marks. Suggested Readings: 1. Bala, Raj (1986), Urbanisation in India, Rawat Publishers, Jaipur. 2. Bansal, S.C. (2008), Urban Geography (Hindi Edition), Meenakshi Prakashan, Meerut. 3. Bansal, S.C. (2010), Urban Geography, Meenakshi Prakashan, Meerut. 4. Cadwallader, Martin (1986), Urban Geography, Prentic Hall, New Jersey. 5. Carter, Harold (1995), The Study of Urban Geography (4th Edition), Arnold, London. 6. Dickinson, R.E. (1964), City and Region, Routledge, London. 7. Kundu, A (1992), Urban Development and Urban Research in India, Khanna Publication, New Delhi. 8. Mayer H.M. and Kohn, C.F. (eds.) (1958), Readings in Urban Geography, University of Chicago Press, Chicago. 9. Pacione, Michael (2001), Urban Geography-A Global Perspective, Routedge, London, 10. Ramachandran, R. (1989), Urbanisation and Urban Systems in India, Oxford, New Delhi. 11. Rao, B.P. and Sharma, N. (2000-01), Urban Geography (Hindi Edition), Vasundhra Prakashan, Gorkhpur. 12. Singh, K. and Steinberg, F. (eds.) (1987), Urban India in Crisis, New Age International, New Delhi. 13. Smailes, A.E. (1953), The Geography of Towns. Hutchinson, London. M.A. Geography : Semester- I Paper- IV (iii) Geography of Rural Settlement End Semester Exam : 80 marks Internal Assessment : 20 marks Total : 100 marks Time : 3 hrs. UNIT-I Definition, nature and scope of rural settlement geography; trends in rural settlement geography with special reference to India; Approaches to rural settlement geography UNIT-II Culture-Historical Perspective: Archaeological finds and settlements; Mesopotamia, the Nile valley, the Indus valley, Historical development of rural settlements (based on major cultural periods) in India, Analysis of Place Names and Environments. UNIT-III Morphology of Rural settlements in India: Religio-ritual model, Secular-dominance model, Types and Patterns of rural settlements in India and causes of diverse types of rural settlements. UNIT-IV Functions of rural settlements, Rural Service Centers- their nature and hierarchy, Basics of Rural Settlement Planning, Rural Settlement Planning of India. Note: The question paper will have five units. Each of the first four units of question paper will contain two questions from each unit of the syllabus. Candidate(s) are required to attempt one question from each unit. The unit five shall be compulsory and shall contain eight short answer type questions covering entire syllabus. All questions carry equal marks. Recommended Readings: 1. Alam, S. M. et. al. (1982), Settlement System of India, Oxford and IBH Publication Co. New Delhi. 2. Chisholm, M. ( 1967), Rural Settlements and Land Use, John Wiley, New York. 3. Clout, H.D. (1977) Rural Geography of Settlements, Mac Donald & Evans, New York. 4. Hudson, F.S. (1976), A Geography of Settlements, Mac Donald & evans, New York. 5. Mandal, R.B. (1988), System to Rural Settlements in Developed Countries, Concept Publication, New Delhi. 6. Mandal, R.B. (2001), Introduction to Rural Settlements, Concept Publication, New Delhi. 7. Misra, H.N. (1987) Rural Georaphy, Vol. IX, Contributions to Indian Geography, Heritage Publishers, New Delhi. 8. Singh, R.L. and K.N. eds. (1975), Readings in Rural Settlements Geography, NGSI, Varanasi 9. Singh, R.L. (1976), Geographic Dimensions of Rural Settlements, NGSI, Varanasi 10 Singh, R.Y.(1994), Settlements, NGSI, Varanasi. 11. Singh, R.Y. (2005), Adhiwas Bhugol, (in Hindi) Rawat Publication, New Delhi. 12. Wanmali, S. (1983), Service Centres in Rural India, B.R. Publication, New Delhi. M.A. Geography: Semester-I Paper-IV (iv) Cultural Geography End Semester Exam : 80 marks Internal Assessment : 20 marks Total : 100 marks Time : 3 hrs. Unit-I The Nature Meaning &Scope of Cultural Geography. The evolutionary approach in cultural geography. The Framework of cultural Geography. The evolution of cultural Geography-The contribution of otto schluter and carl sauer and others. Themes in cultural Geography-The Cultural Region. Functional Formal and perceptual Determinism and Possibilism. Unit-II Cultural Geography : Elements& Components; Culture Areas & Cultural Realm. Environment and Culture, Concept of culture areas and culture regions, Dwelling places as cultural expressions. Role of Environment in the Development of Folk Culture and its Diversity, Revival of Folk Culture. Cultural Adaptation and Environmental perception. Man as modifier of the earth Unit-II spatial structure. Focuses on similarities and differences of various cultures with respect to racial, ethnic, religious, linguistic, demographic, and organizational characteristics in Indian context. Studies of the socio-cultural characteristics of contemporary societies within their manifested Unit-IV Human races , Habitat economy and Society of tribal groups. Racial Elements in India's Population; Tribes of India ( Bhil, Gond, Toda, Naga); Tribes of World (Eskimo, Pigmy, Bushman). Role of Environment in the Development of Folk Culture and its Diversity, Revival of Folk Culture, Patterns of popular Culture and Cultural fusion Note: The question paper will have five units. Each of the first four units of question paper will contain two questions from each unit of the syllabus. Candidate(s)are required to attempt one question from each unit. The unit five shall be compulsory and shall contain eight short answer type questions covering entire syllabus.All questions carry equal marks. Suggested Readings: Ahmad, Aijazuddin, Social Geography, Rawat Publication, New Delhi, 1999 . De Blij. B.d. Human Geography. John Wiley and Son, New York. Dreze Jean, Amartya Sen, Economic Development and Social Opportunity, Oxford University press, New Delhi,1996 . Dubey, S.C.: Indian Society, National Book Trust, New Delhi, 1991. Gregory, D. and UJ. Larry. (eds.) Social relations and Spatial Structures, McMillan, 1985 Haq, Mahbubul: Reflection on Human Development. Oxford University Press.New Delhi Maloney, Clarence: People of South Asia, Winston, New York, 1974 . Planning Commission, Government of India: Report on Development of Tribal areas.1981 Rao, M.S.A.: Urban Sociology in India. Orient Longman, 1970 . Schwartzberg Joseph: An Historical Atlas of South Asia. University of Chicago Press. Chicago, 1978 . Sen, Amartya and Dreze Jean, Indian Development Selected Regional Perspectives. Oxford University Press,1996 . Smith, David: Geography: A Welfare Approach. Edward Arnold, London, 1977 . Sopher, David: An Exploration of India. Cornell University Press. 1980 . Subba Rao. personality of India: Pre and Proto Historic Foundation of India and Pakistan, M.S. University, Baroda, Vadodara, 1958. For more here is the attachment. |
| 7th June 2015 10:02 AM | |
| Unregistered | MDU Rohtak MA Geography Syllabus Will you please provide here the syllabus of the MA Geography course offered by the MDU Rohtak .please give syllabus in PDF file . |