|
#2
8th August 2015, 10:47 AM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Karnataka State Open University Msc Microbiology
As you are looking for the M.sc microbiology syllabus for the Karnataka state open university so here I am providing you the syllabus alonmg with some details : Duration: It is an 2 Years duration course. Eligibility Criteria: A pass in 3 Yrs Degree from Recognized University in Bsc. Fees: For Msc in Microbiology fees is Rs 6000 per semester. Exam Fees; Rs. 1500 Registration fees of the course: Rs 500 (one time) syllabus of Msc in Microbiology :- 1st Semester Human Anatomy Human Physiology Clinical Bio Chemistry Histopathology Introductory Biology Communication and Soft Skills Practical 2nd Semester General Bacteriology Immunology Hematology Basic Cellular Pathology Practical 3rd Semester Systematic Bacteriology Applied Microbiology Microbial Molecular Genetics Molecular Biology Practical 4th Semester Virology Mycology Parasitology Research Methodology & Techniques Practical And here I am providing you the detailed syllabus of MSC Microbilogy; MSC Microbilogy KSOU word file 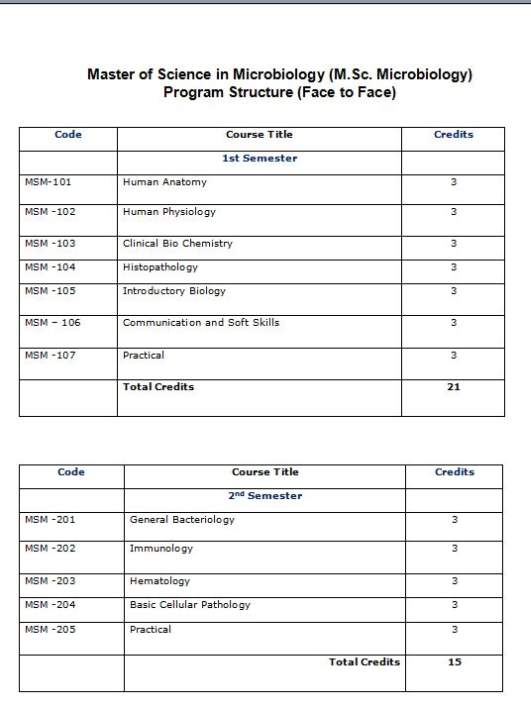  Block1 Unit 1 1-Introduction of anatomy and Histology, 2-Elementary Histology of cell, 3-Tissues of the body organs and system, Unit 2 1- Elementary Anatomy and Histology of Skeletal System. 2- Development of bones, types of bones, 3- Micro-anatomical and gross structure of bones, Unit 3 1- Osteology of human skeleton and various movement of joiints. 2- Muscular System Structure and type of muscles in human body, important muscles and their group action. 3- Circulation System Structure of heart and blood vessels, Systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation, Portal circulation, and coronary circulation. Unit 4 1- Lymphatic System Lymph vessels, Lymph nodes and Lymphoid organs, their structure and functions. 2- Digestive System Gastrointestinal tract and associated glands (Salivery Glands, Liver, Pancreas etc). 3- Respiratory System Trachea, Lungs including other air passages. Block 2 Unit 1 1-Urinary System Kidney, urethra and urinary bladder etc. 2-Endocrine System -Thyroid glands, Parathyroid glands, Adrenal glands and Pituitary glands. 3-Female and Male reproductory organs System. Unit-2 1- Skin and its appendages, 2- Special sense organs: Eye, Ear, Nose Taste buds, Subcutaneous sense organs. 3- Nervous System: Brain, Spinal cord and peripheral nerves. Unit –3 Respiratory Organs: • Nasopharynx • Or pharynx • Larynx • Trachea • Bronchi • Lungs (and their lobular segments) Unit-4 1- Surface Markings of the Body: • Nine regions of the abdomen • Four quadrants of the Hip 2- Introduction of different Vital Organs: Block 3 Unit 1 Respiratory Organs: • Nasopharynx • Or pharynx • Larynx • Trachea Unit 2 • Bronchi • Lungs (and their lobular segments) • Thoracic cavity • Pleura and Pleural cavity Unit 3 Circulatory Organs • Anatomical position of the heart • Pericardium of the heart • Chambers of the heart Unit 4 • Great vessels of the heart • Valves of the heart MSM-102: Human Physiology Total Credit : 3 Block 1 Unit 1 1- Introduction Physiology 2- Brief description of Physiology 3- Terms used in Physiology 4- System of the body Unit 2 1- The body fluids 2- Tissue fluids exchange 3- Odema and Swelling Unit 3 1- Cell structure 2- Cell division 3- Function of Cell 4- Reproduction Unit 4 Brief Description 1- Ear 2- Nose 3- Eyes Block 2 Unit 1 1- Introduction of Tissue 2- Function of Tissues 3- Types of Tissue 4- Introduction of Cartilages Unit 2 The important physico-chemical laws applied to physiology 1- Diffusion 2- Osmosis 3- Bonding 4- Filtration 5- Dialysis 6- Surface Tension 7- Adsorption 8- Colloid Unit 3 1- Neuron and its function, spinal cord and reflex action, 2- sensory end organs and sensory path ways, cerebral cortex and motor path ways. 3- Maintenance of posture and locomotion, automatic nervous system, Physiology of vision, hearing test and olfaction. Unit4 1- Types of muscles, innervations of muscles, 2- Neuromuscular transmission, 3- Mechanism of muscular contraction. Block 3 Unit 1 Cardiovascular System 1- Anatomy and Physiology of Heart, 2- Define and function of Veins and arteries in the circulatory system 3- Circulation-systematic and pulmonary (In brief). 4- Brief review of chamber of Heart- the cardiac cycle Unit 2 Digestive System 1- Physiology and Anatomy of mouth, pharynx, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, Absorption of food and its excretion. 2- Role of Bile in Digestion and Excretion 3- Brief description of Liver and function Unit 3 Respiratory System 1- Brief description of Larynx, Trachea and 2- Brief description of Lungs. 3- Respiratory movement and rate of Respiration Unit 4 Urinary System A) Structure and functions of Kidney, Uretures, Bladder, Urethra and Nephron. B) Composition of normal urine. C) Related Diseases- Cystitis, Nephritis, Pyelonephritis D) Disorder of micturition, renal failure, uraemia MSM-103: Clinical Biochemistry Total Credit: 3 Block 1 Unit 1 1- Laboratory management and planning, 2- Reception and recording of specimens, Cataloging and indexing, 3- Maintenance of laboratory records. Unit 2 1- Knowledge of calibration and volumetric glass wares the underlying principles, care and use of analytical balance, electrical balance, 2- Photoelectric colorimeters, flame Phottometer,PH meter,Absorptionmeter,Visual 3- Colorimeters,Spectrometers,and Electrophoretic apparatus. Unit 3 1- Stiring and cleaning of glass wares knowledge of common types of pipettes,Flasks ,Funnels, other glass waes and Kipp’s apparatus etc. 2- Anticoagulants,collection and preservation of specimens. 3- Basic knowledge of Physical Chemistry: Atom ,molecule ,valancy,ion,atomic weight,molecular weight,acid,base salt-acidimetrty and alkalimetry,reduction,and ionization.Basic knowledge of element,metals and non-metals,their compund and salts,organic solvents,cobohydrates,fats,protein,aminoacids,urea ,uric acid and enzyme,indicators. Symbols of molecular weight of somecommonly used compounds-Acetric acid,Amonium Hydroxide,clcium chloride copper Sulphate hydrochloric acid Nitric acid sodium carbonate sodium chloride, Sodium Hydroxide,Sulphuric acid,carbon,Cholride,Hydrogen,Oxygen,Nitogen,Phosp horus,Pottasium Silver,Sodium and Sulpher. Unit 4 1- Molar Normal and Abnormal solutions ,PH buffer solutions acid Preseration of common solutions,Gravimetric and Volumetric methods,Electrophoresis. 2-Chemical Examination of Urine for Protin,Sugar,Blood,Ketone bodies,Bile Pigment and salt,Urobillinogen,Calcium Chloride etc Preparation of solutions, 3-Principle ,Specimen,Procedure Calculation ,normal value of each tests. Block -2 Unit 1 1- Preparation of Protin free Filtrate, Liver function test: Serum Bilirubin (Direct, Indirect & Total) SGOT, SGPT ,ALP,S.PROTEIN ,S.ALBUMIN,SERUM GLOBULIN d.Serum S.albumine.SGlobulin. - 2-Lipids: 1Serium Cholesterol 3- Glucose Metabolism:. Blood sugar fasting and post prendal-(Toluidine methods folin –wu and Glucose oxidase methods) b .Glucose Tolerance test c. Urine Glucose. Unit 2 1- Carbohydrate.: nomenclature, classification and properties. 2- Amino acid : Classification, Essential and nonessential amino acids 3- Protein : Definition, classification and structure Unit 3 1- Mechanism of Glycolysis and its regulation. 2- Mechanism of Glycogenesis 3- Mechanism of Glyconeogenesis. Unit 4 1- Mechanism of Kreb’s and Cori’s cycle. 2- Mechanism of Blood sugar regulation and glycosuria. 3- Glucose tolrence test. Block 3 Unit 1 1- Deamination and Trasamination of Protein. 2- Urea formation. 3- Creatine Metabolism. Unit 2 1- De finition and importence of B oxidation of fatty acid. 2- Function and clinical improtence of Triglycrol. 3- Function and importence of calcium. Unit 3 1- Blood: composition ,Function and sepration of Plasma protein, Blood coagulation 2- Chemeistry and function of hemoglobin including porphyrin,and bilirubin metabolism. 3- Metabolic disorders: Dialysis Unit4 1- Structure and function of purine and pyrimidine . 2- Role of nucleic acid in genetic engineering. 3- Metabolism of Purine synthesis. |