|
#4
28th February 2015, 12:47 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: DRDO STA B mechanical Engineering Exam Question Paper
As per your request, I am giving you DRDO STA B Mechanical engineering paper. have a look. 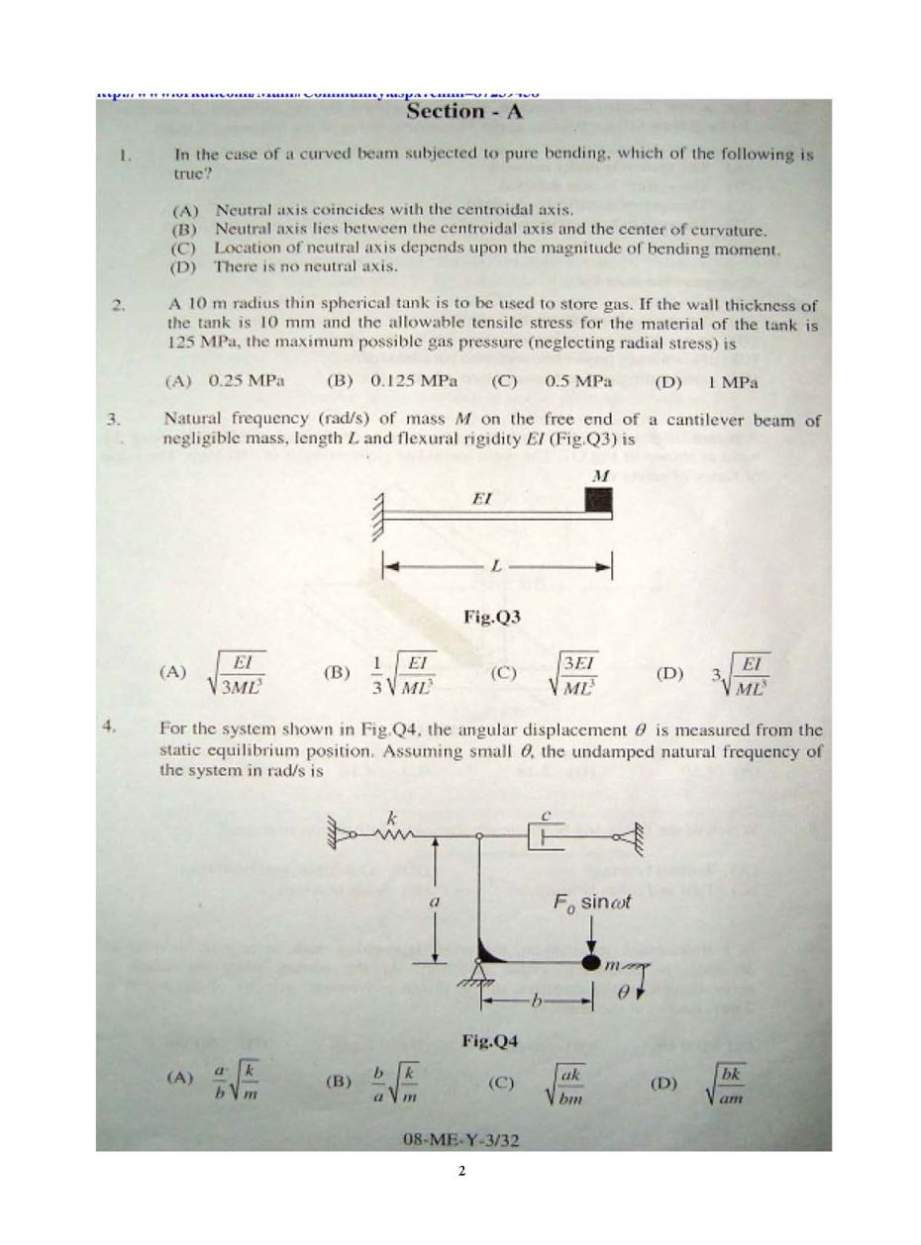    Here, I am giving you syllabus of the DRDO STA B mechanical Engineering. Engineering Mechanics: Free body diagrams and equilibrium; trusses and frames; virtual work; kinematics and dynamics of particles and of rigid bodies in plane motion, including impulse and momentum (linear and angular) and energy formulations; impact. Strength of Materials: Stress and strain, stress-strain relationship and elastic constants, Mohr’s circle for plane stress and plane strain, thin cylinders; shear force and bending moment diagrams; bending and shear stresses; deflection of beams; torsion of circular shafts; Euler’s theory of columns; strain energy methods; thermal stresses. Theory of Machines: Displacement, velocity and acceleration analysis of plane mechanisms; dynamic analysis of slider-crank mechanism; gear trains; flywheels. Vibrations: Free and forced vibration of single degree of freedom systems; effect of damping; vibration isolation; resonance, critical speeds of shafts. Design: Design for static and dynamic loading; failure theories; fatigue strength and the S-N diagram; principles of the design of machine elements such as bolted, riveted and welded joints, shafts, spur gears, rolling and sliding contact bearings, brakes and clutches. Fluid Mechanics: Fluid properties; fluid statics, manometry, buoyancy; control-volume analysis of mass, momentum and energy; fluid acceleration; differential equations of continuity and momentum; Bernoulli’s equation; viscous flow of incompressible fluids; boundary layer; elementary turbulent flow; flow through pipes, head losses in pipes, bends etc. Heat-Transfer: Modes of heat transfer; one dimensional heat conduction, resistance concept, electrical analogy, unsteady heat conduction, fins; dimensionless parameters in free and forced convective heat transfer, various correlations for heat transfer in flow over flat plates and through pipes; thermal boundary layer; effect of turbulence; radiative heat transfer, black and grey surfaces, shape factors, network analysis; heat exchanger performance, LMTD and NTU methods. Thermodynamics: Zeroth, First and Second laws of thermodynamics; thermodynamic system and processes; Carnot cycle. irreversibility and availability; behaviour of ideal and real gases, properties of pure substances, calculation of work and heat in ideal processes; analysis of thermodynamic cycles related to energy conversion. Applications: Power Engineering: Steam Tables, Rankine, Brayton cycles with regeneration and reheat. I.C. Engines: air-standard Otto, Diesel cycles. Refrigeration and air-conditioning: Vapour refrigeration cycle, heat pumps, gas refrigeration, Reverse Brayton cycle; moist air: psychrometric chart, basic psychrometric processes. Turbomachinery: Pelton-wheel, Francis and Kaplan turbines — impulse and reaction principles, velocity diagrams. Engineering Materials: Structure and properties of engineering materials, heat treatment, stress-strain diagrams for engineering materials. Metal Casting: Design of patterns, moulds and cores; solidification and cooling; riser and gating design, design considerations. Forming: Plastic deformation and yield criteria; fundamentals of hot and cold working processes; load estimation for bulk (forging, rolling, extrusion, drawing) and sheet (shearing, deep drawing, bending) metal forming processes; principles of powder metallurgy. Joining: Physics of welding, brazing and soldering; adhesive bonding; design considerations in welding. Machining and Machine Tool Operations: Mechanics of machining, single and multi-point cutting tools, tool geometry and materials, tool life and wear; economics of machining; principles of non-traditional machining processes; principles of work holding, principles of design of jigs and fixtures |