|
#4
19th February 2016, 08:26 AM
| |||
| |||
| Re: UPSC Civil Services Electrical Engineering
Friend Have a Look , Here I am Providing Electrical Engineering Syllabus for UPSC Main Examination : For Exam pattern Image : 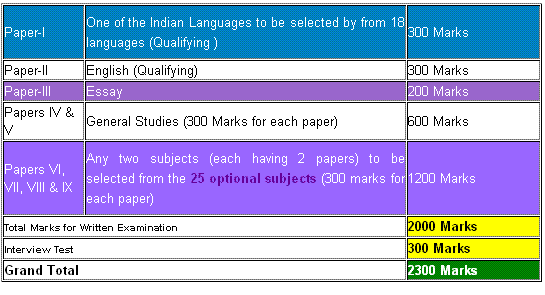 Syllabus for UPSC Main Electrical Engineering Examination : Paper-I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis; basic network theorems and applications; transient analysis: RL, RC and RLC circuits; sinusoidal steady state analysis; resonant circuits; coupled circuits; balanced 3-phase circuits; Two-port networks. 2 . Signals & Systems: Representation of continuous-time and discrete-time signals & systems; LTI systems; convolution; impulse response; time-domain analysis of LTI systems based on convolution and differential/difference equations. Fourier transform, Laplace transform, Z-transform, Transfer function. Sampling and recovery of signals DFT, FFT Processing of analog signals through discrete-time systems. 3 . E.M. Theory: Maxwell's equations, wave propagation in bounded media. Boundary conditions, reflection and refraction of plane waves. Transmission line: travelling and standing waves, impedance matching, Smith chart. 4 . Analog Electronics: Characteristics and equivalent circuits (large and small-signal) of Diode, BJT, JFET and MOSFET. Diode circuits: clipping, clamping, rectifier. Biasing and bias stability. FET amplifiers. Current mirror; Amplifiers: single and multi-stage, differential, operational, feedback and power. Analysis of amplifiers; frequencyresponse of amplifiers. OPAMP circuits. Filters; sinusoidal oscillators: criterion for oscillation; single-transistor and OPAMP configurations. Function generators and wave-shaping circuits. Linear and switching power supplies. 5 . Digital Electronics: Boolean algebra; minimization of Boolean functions; logic gates; digital IC families (DTL, TTL, ECL, MOS, CMOS). Combina-tional circuits: arithmetic circuits, code converters, multiplexers and decoders. Sequential circuits: latches and flip-flops, counters and shift-registers. Comparators, timers, multivibrators. Sample and hold circuits, ADCs and DACs. Semiconductor memories. Logic implementation using programmable devices (ROM, PLA, FPGA). 6 . Energy Conversion: Principles of electromechanical energy conversion: Torque and emf in rotating machines. DC machines: characteristics and performance analysis; starting and speed control of motors; Transformers: principles of operation and analysis; regulation, efficiency; 3-phase transformers. 3-phase induction machines and synchronous machines: characteristics and preformance analysis; speed control. 7 . Power Electronics and Electric Drives: Semiconductor power devices: diode, transistor, thyristor, triac, GTO and MOSFET-static characteristics and principles of operation; triggering circuits; phase control rectifiers; bridge converters: fullycontrolled and half-controlled; principles of thyristor choppers and inverters; DCDC converters; Switch mode inverter; basic concepts of speed control of dc and ac Motor drives applications of variablespeed drives. 8 . Analog Communication: Random variables: continuous, discrete; probability, probability functions. Statistical averages; probability models; Random signals and noise: white noise, noise equivalent bandwidth; signal transmission with noise; signal to noise ratio. Linear CW modulation: Amplitude modulation: DSB, DSB-SC and SSB. Modulators and Demodulators; Phase and Frequency modulation: PM & FM signals; narrowband FM; generation & detection of FM and PM, Deemphasis, Preemphasis. CW modulation system: Superhetrodyne receivers, AM receivers, communication receivers, FM receivers, phase locked loop, SSB receiver Signal to noise ratio calculation for AM and FM receivers. Paper-II 1 . Control Systems: Elements of control systems; block-diagram representation; open-loop & closedloop systems; principles and applications of feed-back. Control system components. LTI systems: time-domain and transform-domain analysis. Stability: Routh Hurwitz criterion, root-loci, Bodeplots and polar plots, Nyquist's criterion; Design of lead-lad compensators. Proportional, PI, PID controllers. Statevariable representation and analysis of control systems. 2 . Microprocessors and Microcomputers: PC organisation; CPU, instruction set, register set, timing diagram, programming, interrupts, memory interfacing, I/O interfacing, programmable peripheral devices. 3 . Measurement and Instrumentation: Error analysis; measurement of current, voltage, power, energy, power-factor, resistance, inductance, capacitance and frequency; bridge measurement. Signal conditioning circuit; Electronic measuring instruments: multimeter, CRO, digital voltmeter, frequency counter, Q-meter, spectrum-analyzer, distortion-meter. Transducers: thermocouple, thermistor, LVDT, strain-gauge, piezo-electric crystal. 4 . Power Systems: Analysis and Control: Steady-state performance of overhead transmission lines and cables; principles of active and reactive power transfer and distribution; per-unit quantities; bus admittance and impedance matrices; load flow; voltage control and power factor correction; economic operation; symme-trical components, analysis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults. Concept of system stability: swing curves and equal area criterion. Static VAR system. Basic concepts of HVDC transmission. 5 . Power System Protection: Principles of overcurrent, differential and distance protection. Concept of solid state relays. Circuit breakers. Computer aided protection: Introduction; line bus, generator, transformer protection; numeric relays and application of DSP to protection. 6 . Digital Communication: Pulse code modulation (PCM), differential pulse code modulation (DPCM), delta modulation (DM), Digital modulation and demodulation schemes: amplitude, phase and frequency keying schemes (ASK, PSK, FSK). Error control coding: error detection and correction, linear block codes, convolution codes. Information measure and source coding. Data networks, 7-layer architecture. |