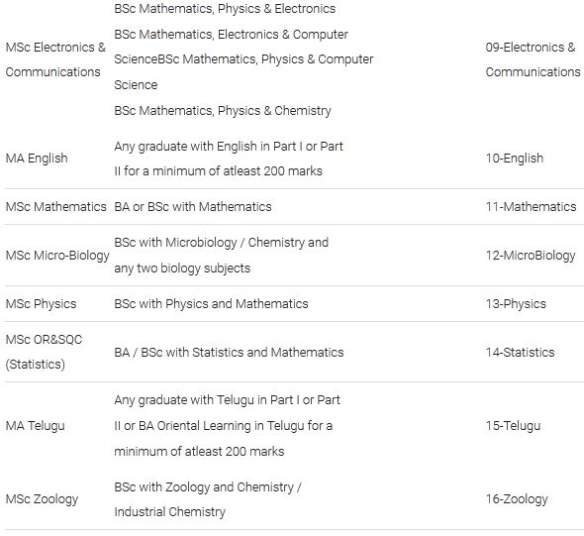
| Re: Rayalaseema University PG CET
The syllabus for RUPGCET (Rayalaseema University Post-Graduate Common Entrance Test) for admission in M.A.(Political Science) Program is as follows:
SECTION – A: PAPER-I: BASIC CONCEPTS OF POLITICAL SCIENCE
Explanatory Frameworks of Politics
1. What is Politics: Nature and Scope of Political Science
2. Approaches to the Study of Politics: Normative, Historical, Empirical Traditions
What is the State
1. Origin and Evolution of the Modern State
2. Different Conceptions on the role of the Modern State: Social Democratic and Neo
Liberal conceptions
Nations and Nationalism
1. Conceptual Distinction between Nationality and Nation
2. Varieties of Nationalism: Culture and Civic Nationalism
Rights and Citizenship
1. Evolution of Rights: Civil and Social rights
2. Citizenship: Universal and Differential Citizenship
Freedom, Equality and Justice
1. Freedom: Negative and Positive Freedom
2. Equality: Formal Equality, Equality of Opportunity, Equality of Outcome
3. Justice: Justice based on Needs, Deserts and Rights
Reference books:
1. Bhargava Rajeev and Acharya Ashok (eds) (2008) Political Theory: An
Introduction, Pearson, New Delhi.
2. Andrew Heywood (2007) Politics 3rd edition, Palgrave Macmillan, NewYork.
3. Bellamy R (1993) (Ed) Theories and Concepts of Politics, Manchester university
press, New York.
4. Vincent A (2004) The Nature of Political Theory, Oxford Universit Press,
NewYork.
SECTION – B: PAPER-II: POLITICAL INSTITUTIONS
(Concepts, Theories and Institutions)
Constitutionalism
1. The Purpose of Constitutional law, Theory of Separation of Powers
2. Structural Forms of the Modern State: Basic features of Parliamentary and
Presidential forms of Government
Territorial Division of Authority of the Modern State
1. Basic features of Federal form of Government
2. Basic features of Unitary form of Government
Institutional forms of the Modern State
1. Democracy: Basic features of Classical and Modern Representative Democracy
2. Models of Democracy: Procedural Democracy and Substantive Democracy
Judiciary and Democratic State
1. The nature, role and functions of the Judiciary
2. Judicial Review: Debates on the Supremacy of legislature or Judiciary in the
protection of Constitutional law
Reference books:
1. Andrew Heywood (2007) Politics 3rd edition, Palgrave Macmillan, New York
2. Held, David (2006) Models of Democracy 3rd edition Oxford Polity Press
3. Birch A.H (2000) The Concepts and Theories of Democracy, London Routledge
4. Bogdanor, V (Ed) (1988) Constitutions in Democratic Politics Gower, Aldershot
5. Scott Gordon (1999) Controlling the State: Constitutionalism from Ancient Athens to
Today, Cambridge, Harvard University Press.
SECTION – C: PAPER-III: INDIAN CONSTITUTION
The Making of the Constitution
1. The ideological legacy of the Indian National Movement on the Constituent
Assembly
2. The Nature and Composition of the Constituent Assembly
Philosophical Premises of the Indian Constitution
1. Preamble: The underlying values of the Indian Constitution
2. Salient features of the Constitution of India
Fundamental rights and Directive principles of State Policy
1. Individual and Collective Rights: Limitations on the fundamental Rights
2. Judicial Interpretation of Fundamental Rights
3. The doctrine of ‘Basic Structure’ of the Constitution: KesavanandaBharathi Case
Indian Federalism
1. Unitary and Federal features in the Indian Constitution
2. Tension Areas between the Union and State Governments
Legislative, Administrative and Financial Spheres
Working of the Indian Constitution
1. The Values of the Indian Constitution and Ushering of Social Revolution in India
2. The causes for the Ascendency of the Executive over legislature and Judiciary;
Major Controversies regarding the Amendments to the Constitution
3. Nature and Role of Higher Judiciary in India; Recent Debates on the mode of
appointment of Judges
Reference books:
1. Granville Austin (1972) the Indian Constitution, Cornerstone of a Nation Oxford university
Press, New Delhi.
2. Madhavkhosla (2012) the Indian Constitution, oxford university press, New Delhi
3. Granville Austin (1999) Working a Democratic Constitution; A History of the Indian
Experience, Oxford University Press, New Delhi
4. Zoya Hasan, Sridharan E and Sudharshan R (Eds) 2002 India’s living Constitution,
Permanent black, New Delhi
5. BaxiUpendra (1980) the Indian Supreme Court and Politics Eastern book co, Lucknow
|