| 21st May 2015 09:02 AM | |
| Kiran Chandar | Re: What will be the eligibility for IES examination for ECE final year students? Indian Engineering Services IES exam is conducted by Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) in June every year. The IES comprise Group a Services/Posts and Group B Services/ Posts in 4 categories - Civil, Mechanical, Electrical, Electronic and Telecommunications Engineering. IES exam eligibility- Degree in Engineering from recognised University. Passed section A and B of the institution Examinations of the Institution of Engineers (India) or Degree/ diploma in Engineering from foreign university recognized by the government or Passed Graduate Membership Examination of the Institute of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineers (India) Passed Associate Membership Examination Parts II and III/ Sections A and B of the Aeronautical Society of India; or Passed Graduate Membership Examination of the institution of Eletronics and Radion Engineers, London held after November, 1959. Age Limit: Candidate age must be between 21 years to 30 years Upper Age Limit Relaxation: The upper age limit is 35 years for Government Servants and Scheduled Caste or a Scheduled Tribe candidates. 33 years for OBC candidates. 5 years if candidates had ordinarily been domiciled in the State of Jammu & Kashmir during the period from the 01-01-1980-31-12-1989. Nationality: A Candidate must be either i. a citizen of India, or ii. A subject of Nepal, or iii. A subject of Bhutan, or iv.a Tibetan refugee who came over to India before the 01 January , 1962 with the intention of permanently settling in India, or (v). a Person of Indian origin who has migrated from Pakisthan, Burma, Sri Lanka and East African countires of Kenya, Uganda, the United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Malawim Zaire and Ethiopia or Vietnam with the intention of permanently setting in India. Provided that a candidate belonging to categories (ii), (iii), (iv) and (v) above shall be a person in whose favour a certificate of eligibility has been issued by the Government of India. Contact details Union Public Service Commision Man Singh Road Area, New Delhi, Delhi (state) 110069 011 2338 5271 Map location [MAP]Union Public Service Commision New Delhi, Delhi[/MAP] |
| 20th May 2015 05:11 PM | |
| Unregistered | Re: What will be the eligibility for IES examination for ECE final year students? Hi I am the final year students of ECE and I want to apply for IES examination so can I eligible for this exam? |
| 12th August 2014 09:20 AM | |
| Raman Vij | Re: What will be the eligibility for IES examination for ECE final year students? As you want to get the details of what will be the eligibility for IES examination for ECE final year students so here it is for you: Eligibility Criteria: Candidates must have passed graduation in engineering from a recognized university or even final year candidates are also eligible to apply Your age must be in between 21 to 30 years. You must be Indian These Branches are eligible for Exam :- Civil Engineering Mechanical Engineering Electrical Engineering Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Exam Pattern: Screen Shot 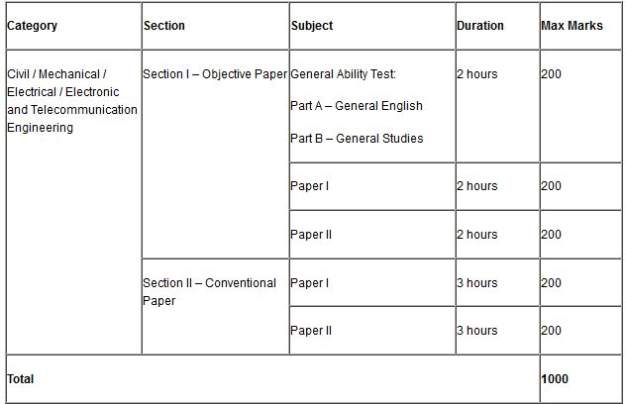 Here for your reference I am giving you the syllabus of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering: Paper I 1. MATERIALS AND COMPONENTS Structure and properties of Electrical Engineering materials; Conductors, Semiconductors and Insulators, magnetic, Ferroelectric, Piezoelectric, Ceramic, Optical and Super-conducting materials. Passive components and characteristics Resistors, Capacitors and Inductors; Ferrites, Quartz crystal Ceramic resonators, Electromagnetic and Electromechanical components. 2. PHYSICAL ELECTRONICS, ELECTRON DEVICES AND ICs Electrons and holes in semiconductors, Carrier Statistics, Mechanism of current flow in a semiconductor, Hall effect; Junction theory; Different types of diodes and their characteristics; Bipolar Junction transistor; Field effect transistors; Power switching devices like SCRs, GTOs, power MOSFETS; Basics of ICs - bipolar, MOS and CMOS types; basic of Opto Electronics. 3. SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS Classification of signals and systems: System modelling in terms of differential and difference equations; State variable representation; Fourier series; Fourier transforms and their application to system analysis; Laplace transforms and their application to system analysis; Convolution and superposition integrals and their applications; Z-transforms and their applications to the analysis and characterisation of discrete time systems; Random signals and probability, Correlation functions; Spectral density; Response of linear system to random inputs. 4. NETWORK THEORY Network analysis techniques; Network theorems, transient response, steady state sinusoidal response; Network graphs and their applications in network analysis; Tellegen’s theorem. Two port networks; Z, Y, h and transmission parameters. Combination of two ports, analysis of common two ports. Network functions : parts of network functions, obtaining a network function from a given part. Transmission criteria : delay and rise time, Elmore’s and other definitions effect of cascading. Elements of network synthesis. 5. ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY Analysis of electrostatic and magnetostatic fields; Laplace’s and Poisson’s equations; Boundary value problems and their solutions; Maxwell’s equations; application to wave propagation in bounded and unbounded media; Transmission lines : basic theory, standing waves, matching applications, microstrip lines; Basics of wave guides and resonators; Elements of antenna theory. 6. ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION Basic concepts, standards and error analysis; Measurements of basic electrical quantities and parameters; Electronic measuring instruments and their principles of working : analog and digital, comparison, characteristics, application. Transducers; Electronic measurements of non electrical quantities like temperature, pressure, humidity etc; basics of telemetry for industrial use. Paper II 1. ANALOG ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Transistor biasing and stabilization. Small signal analysis. Power amplifiers. Frequency response. Wide banding techniques. Feedback amplifiers. Tuned amplifiers. Oscillators. Rectifiers and power supplies. Op Amp, PLL, other linear integrated circuits and applications. Pulse shaping circuits and waveform generators. 2. DIGITAL ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Transistor as a switching element; Boolean algebra, simplification of Boolean functions, Karnaguh map and applications; IC Logic gates and their characteristics; IC logic families : DTL, TTL, ECL, NMOS, PMOS and CMOS gates and their comparison; Combinational logic Circuits; Half adder, Full adder; Digital comparator; Multiplexer Demulti-plexer; ROM an their applications. Flip flops. R-S, J-K, D and T flip-flops; Different types of counters and registers Waveform generators. A/D and D/A converters. Semiconductor memories. 3. CONTROL SYSTEMS Transient and steady state response of control systems; Effect of feedback on stability and sensitivity; Root locus techniques; Frequency response analysis. Concepts of gain and phase margins: Constant-M and Constant-N Nichol’s Chart; Approximation of transient response from Constant-N Nichol’s Chart; Approximation of transient response from closed loop frequency response; Design of Control Systems, Compensators; Industrial controllers. 4. COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS Basic information theory; Modulation and detection in analogue and digital systems; Sampling and data reconstructions; Quantization & coding; Time division and frequency division multiplexing; Equalization; Optical Communication : in free space & fiber optic; Propagation of signals at HF, VHF, UHF and microwave frequency; Satellite Communication. 5. MICROWAVE ENGINEERING Microwave Tubes and solid state devices, Microwave generation and amplifiers, Waveguides and other Microwave Components and Circuits, Microstrip circuits, Microwave Antennas, Microwave Measurements, Masers, lasers; Microwave propagation. Microwave Communication Systems terrestrial and Satellite based. 6. COMPUTER ENGINEERING Number Systems. Data representation; Programming; Elements of a high level programming language PASCAL/C; Use of basic data structures; Fundamentals of computer architecture; Processor design; Control unit design; Memory organisation, I/o System Organisation. Microprocessors : Architecture and instruction set of Microprocessors 8085 and 8086, Assembly language Programming. Microprocessor Based system design : typical examples. Personal computers and their typical uses. |
| 9th August 2014 07:56 AM | |
| Unregistered | What will be the eligibility for IES examination for ECE final year students? I am in ECE final year and I want to give the exam of IES and for that I want to get the details of what will be the eligibility for IES examination for ECE final year students so can you provide me that? |