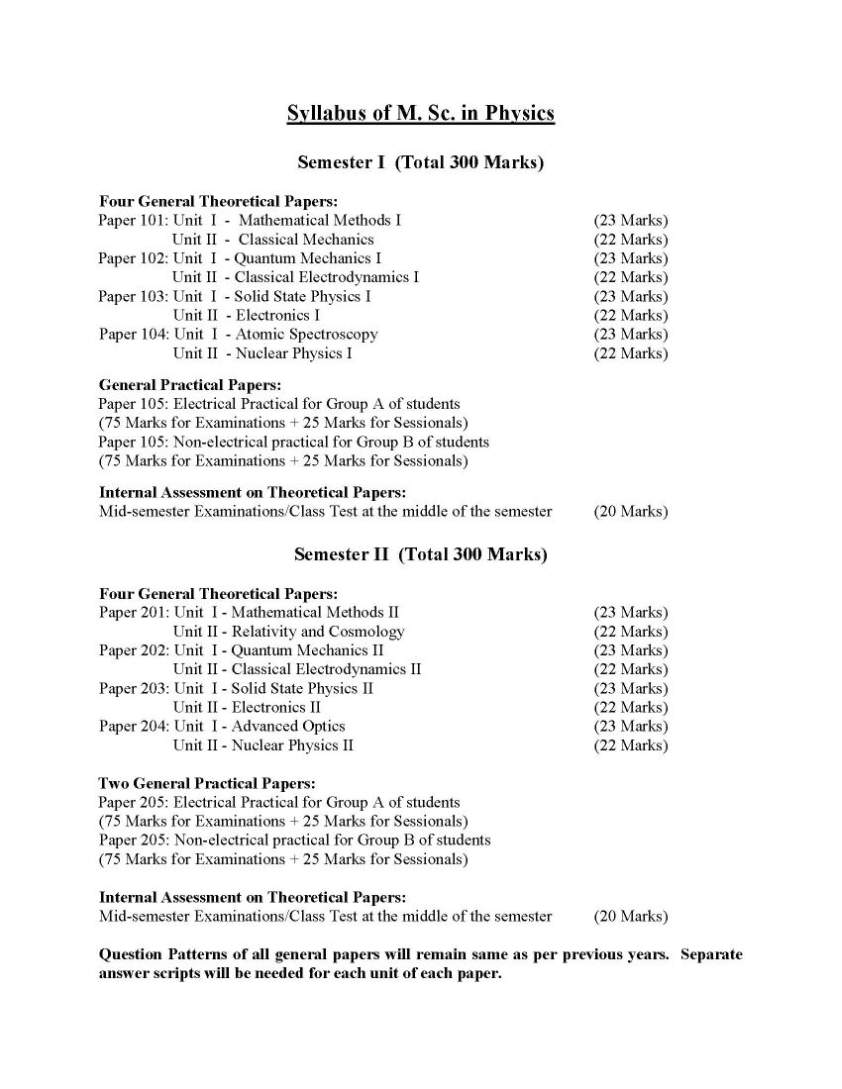
| Re: MSc Physics Syllabus
As you want to get MSc Physics Syllabus of Pune University so here I am providing you same:
Revised Syllabus
PHYUT501 CLASSICAL MECHANICS
1 Constrained Motion
Constraints, Classification of Constraints, Principal of Virtual Work, D’Alembert’s
principal and its applications (Problems only), (One or Two Problems should be discussed
with D’Alembert’s, Lagrangian, Hamiltons from same set of problems). (2L+2P)
.
2 Lagrangian formulation
Generalized coordinates, Langrange’s equations of motion, properties of kinetic
energy function, theorem on total energy, generalized momenta, cyclic-coordinates, integrals
of motion, Jacobi integrals and energy conservation, Concept of symmetry, invariance under
Galilean transformation, velocity dependent potential. (6L+5P)
3 Hamilton’s formulation
Hamilton’s function and Hamilton’s equation of motion, configuration space, phase
space and state space, Lagrangian and Hamiltonian of relativistic particles and light rays.
(3L+4P)
4 Variational Principle
Variational principle, Euler’s equation, applications of variational principle, shortest
distance problem, brachistrochrone, Geodesics of a Sphere. (3L+2P)
5 Canonical Transformations
Generating function, Conditions for canonical transformation and problem. (3L+2P)
6 Poisson Brackets
Definition, Identities, Poisson theorem, Jacobi-Poisson theorem, Jacobi identity,
(statement only), invariance of PB under canonical transformation. (2L+3P)
7 Rotational Motion
Rotating frames of reference, inertial forces in rotating frames, Larmour precision,
electromagnetic analogy of inertial forces, effects of Coriolis force, Focoult’s pendulum.
(3L+3P)
8 Central Force
Two body central force problem, stability of orbits, condition for closure, integrable
power laws, Kepler’s problems, orbits of artificial satellites, Virial theorem. (3L+2P)
Reference Books :
1. Classical Mechanics by H.Goldstein, Narosa Publishing Home,, New Delhi.
2. Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems by Marion and Thomtron, Third Edition,
Horoloma Book Jovanovich College Publisher.
3. Classical Mechanics by P.V.Panat, Narosa Publishing Home,, New Delhi.
4. Classical Mechanics by N.C.Rana and P.S.Joag, Tata Mc-Graw Hill Publishing Company
Limited, New Delhi.
5. Introduction to Classical Mechanics by R.G.Takawale and P.S.Puranik, Tata Mc-Graw
Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi.
6. Classical Mechanics by J.C.Upadhyaya, Himalaya Publishing House.
Revised Syllabus
PHYUT502 ELECTRONICS
1.Study of Operational Amplifiers :
1.1 Concept of input/output impedance, Input bias current, offset input voltage, slew rate, CMMR,
Gain, frequency response, Band Width in different types of OP-AMPs such as BJT, JFET,
MOS FET.
1.2 Applications of Operational Amplifiers :
a) Active filters : LPF, HPF, BPF, and Notch filter 1st and 2nd order with designing
( Concept of Roll off, octave, Decade)
b) Instrumentation Amplifier
c) Function Generator – Square wave, triangular, sawtooth , sine wave.
d) Half wave and full wave precision rectifiers.
e) Sample and hold circuits. (10L)
2. Power Supply :
2.1 Concept of current limit, fold back current limiting, constant voltage constant current (CVCC)
using IC-723.
2.2 Three terminal adjustable regulator.
2.3 Switching regulator using TL 494 (Texas Instruments)
2.4 Concept of DC to DC converter.
2.5 Introduction to UPS and Inverters. (10L)
3.Combinational Logic :
3.1 Logic Identities
3.2 Minimization and Karnaugh map ( upto 4 variables)
3.3 Combinational functions available as ICs.
3.4 Programmable logic devices : PLA (TIF PLA 840) (3L)
4. Sequential Logic :
4.1 Monostable multivibrator - IC 74121, 74123, 555
4.2 Counters – BCD, Binary, up-down counter.
4.3 Shift registers : SISO, SIPO, PISO, PIPO, using IC 7495. (8L)
5.Special Function IC’s :
5.1 Voltage Controlled Oscillator – IC 566.
5.2 Function Generator – IC 8038.
5.3 Phase Locked Loop PLL – IC 565. (6L)
6. Data Converter :
6.1 DAC : Characteristics, R-2R and Binary type.
6.2 ADC : Characteristics, Dual type, Simultaneous type, Successive Approximation and
Counter type.
6.3 Multiplexer and Demultiplexer. (8L)
7. Introduction to terms used in Frontiers of Electronics :
7.1 Frequency Spectrum : MW, SW, FM, LHF, VHF, UHF, Microwave.
7.2 Communication : Modulation, Demodulation, Optical Fiber Communication(OFC),
satellite communication – uplink & downlink, cellular phone, Internet, Modem, Wi-Fi,
Radar. (3L)
Note :
1. Designing problems are expected to be worked out for respective topics.
2. Student should refer manuals for data specifications.
Reference Books :
1. Operational Amplifiers – G.B.Clayton (5th edition ) Newnes
2. Operational Amplifiers Applications – G.B.Clayton
3. Electronic Principles – Malvino (TMH Publication)
4. Operational Amplifiers – Subrahmanyam
5. Op-amps and Linear Integrated circuits – Gayakwad (Prentice Hall)
6. Linear Integrated circuits – D.Roy Choudhury, Shail Jain
7. Power Supplies – B.S.Sonde
8. Power Electronics – P.C.Sen
9. SMPS Inverters Converters : Gottlib
10. Integrated circuits – Botkar
11. Digital Principles and Applications : Leach and Malvino
12. Data Converters – B.S. Sonde.
Revised Syllabus
PHYUT503 MATHEMATICAL METHODS IN PHYSICS
1. Complex Analysis :
Analytical functions, Cauchy-Riemann conditions, Line integrals, Cauchy’s theorem,
Cauchy integral formula, Derivatives of analytical functions, Power Series, Taylor’s theorem,
Laurent’s theorem, Calculus of residues, revaluation of real definite integrals.
Ref. 1 - , Ch2, to 7 , Ref. 2 (6L + 4 T)
2. Linear spaces and operators :
Vector spaces and subspaces, Linear dependence and independence, Basis and
Dimensions, linear operators, Inverses, Matrix representation, Similarity transformations, Eigenvalues
and eigenvectors, Inner product, Orthogonality, Introduction only to Gramm-Schmidt orthogonalization
procedure, Self adjoint and Unitary transformations, Eigenvalues & eigenvectors of termitian &
Unitary transformations, Diagonalization.
Ref. 3 ( Ch. 3 & 4) , Ref 5. (12L + 2T)
3. Special Function :
Legendre Hermite, Laguerre function – Generating function, Recurrence relations and
their differential equations Orthogonality properties, Bessels’s function of first kind , Spherical Bessel
function, Associated Legendre function, Spherical harmonics.
Ref 4, Ref. 7. ( 10L + 2T)
4. Fourier Series and Integral transforms :
Fourier Series : Definition, Dirichlet’s condition, Convergence, Fourier Integral and
Fourier transform, Convolution theorem, Parseral’s identity, Applications to the solution of differential
equations, Laplace transform and its properties, Applications to the solution of differential equations,
Fourier transform & Laplace transform of Dirac Delta function.
Ref. 4, Ref. 6. ( 8L + 4T)
Reference Books :
1. Complex Variables and Applications – J.W.Brown, R.V.Churchill – (7th Edition)-
Mc-Graw Hill – Ch. 2 to 7.
2. Complex Variables – Seymour Lipschutz
3. Mathematics of Classical and Quantum Physics – Byron, Fuller Dover (1992)
4. Mathematical methods for Physicists – Arfken & Weber – 6th Edition-Academic Press- N.Y.
5. Linear Algebra – Seymour Lipschutz, Schaum Outlines Series- Mc-Graw Hill edition
6. Mathematics for Physical Sciences – Mary Boas, John Wiley & Sons
7. Mathematical Methods of Physics – Mathews & Walker – 2nd Edition- Pearson Edition
8. Fourier Series - Seymour Lipschutz, Schaum Outlines Series
9. Laplace Transform - Seymour Lipschutz, Schaum Outlines Series
10. Mathematical Methods in Classical and Quantum Physics – Tulsi Das, S.K.Sharma-
University Press India.
11. Mathematical Methods in Physics – Butkov Addiddion Wesley Publishers.
12. Advanced Engineering Mathematics, E. Kreyszig, 7th Edition, New Age International
13. Matrices and Tensors in Physics, A. W. Joshi, 3rd Edition, New Age International
Revised Syllabus
PHYUT 504 QUANTUM MECHANICS – I
1. Revision of the following topics with emphasis on problem solving :
Inadequacy of classical Physics, wave packets and uncertainity relations.
Schrodinger wave equation and probability interpretation, Simple one dimensional problems –
wells, barriers and harmonic oscillator ( One and three dimensional). (6L + 5P)
2. General formalism of Quantum Mechanics :-
Postulates of quantum mechanics :
Representation of states and dynamical variables, observables, self-adjoint operators, eigen
functions and eigen values, degeneracy, Dirac delta function, Completeness and closure property,
Physical interpretation of eigen values, eigen functions and expansion co-efficients, eigen values
and eigen functions of momentum operator.
Hilbert space, Dirac’s bra and ket notation, dynamical variables and linear operators,
projection operators, unit operator, unitary operator, matrix representation of an operator, change of
basis, unitary transformation. Eigen values and eigen functions of simple harmonic oscillator by
operator method. (13L +4P)
Ref. 1. a) Chapter 3 (article 3.1 to 3.10)
b) Chapter 7 (article 7.1 to 7.7)
c) Chapter 4 ( article 4.4)
3. Angular Momentum :
Eigen values and eigen functions of L2 and Lz operators, ladder operators L+ and L-, Pauli
theory of spins( Pauli’s matrices), angular momentum as a generator of infinitesimal rotations, matrix
representation of J in ljm> basis. Addition of angular momenta, Computation of Clebsch-Gordon
co-efficients in simple cases ( J1=1/2, J2=1/2) Central forces with an example of hydrogen atom.
Ref. 1. Chapter 8 ( article 8.1 to 8.3, 8.5, 8.6) (11L+4P)
4. Evolution of system with time :
Constants of motion, Schrodinger and Heisenberg picture, Heisenberg’s matrix mechanics
for harmonic oscillator .
Ref..1. Chapter 3 (article 3.14)
Chapter 9 (article 9.16 to 9.18) (4L +1P)
Reference books :-
1) A Text-book of Quantum Mechanics by P.M.Mathews and K.Venkatesan.
2) Quantum mechanics by A.Ghatak and S.Lokanathan
3) Quantum Mechanics by L.I.Schiff
4) Modern Quantum mechanics by J.J.Sakurai
5) Quantum Physics by R. Eisberg and R.Resnick
6) Introduction to Quantum Mechanics by by David J.Griffiths
7) Introductory Quantum mechanics by Granier, Springer Publication.
8) Introductory Quantum Mechanics, Li boff, 4th Edition, Pearson Education Ltd.
Revised Syllabus
PHYUT601 ELECTRODYNAMICS
1. Multipole expansions and material media :
Multipole expansions for a localised charge distribution in free space, Linear
quadrapole potential and field, static electric and magnetic fields in material media,
Boundary conditions. (4L)
Ref. 1, Ref. 6.
2. Time varying fields :
Time dependents field, Faraday’s law for stationary and moving media,Maxwell’s
displacement current, Differential and Integral forms of Maxwell’s equations, Maxwell’s
equations for moving medium. (6L)
Ref.1, Ref.2, Ref.3, Ref.4
3. Energy, Force and Momentum relations in electromagnetic fields :
Energy relations in quasi-stationary current systems, Magnetic interaction between
two current loops, Energy stored in electric and magnetic fields, Poynting’s theorem,
General expression for electromagnetic energy, Conservation laws.
(6L)
Ref;1, Ref;2, Ref;4, Ref;5, Ref;6, Ref;8
4. Electromagnetic wave equations :
Electromagnetic wave equations,Electromagnetic plane waves in stationary medium ,
Reflection and refraction of electromagnetic waves at plane boundaries (Oblique incidence),
Electromagnetic waves in conducting medium, Skin effect and skin depth. (8L)
Ref. 1; Ref;2, Ref;4, Ref;5, Ref;8
5. Inhomogeneous wave equations :
Inhomogeneous wave equations, Lorentz’s and Coulomb’s gauges, Gauge
transformations, Wave equations in terms of electromagnetic potentials, D’Alembertian
operator, Solutions of inhomogeneous wave equations by Fourier analysis, Hertz potential
and its use in computation of radition fields, Dipole radiation, Radiation energy and
Radiation resistance. (8L)
Ref.1, Ref.2,Ref.4, Ref.5, Ref.8.
6.Relativistic Kinematics:
Experimental basis for special theory of relativity (Michelson – Morley experiment),
Lorentz transformations , Relativistic velocity addition, Mass- Energy relation (E=mc2). (6L)
Ref.1; Ref.2; Ref.3; Ref;7.
7.Covariance and Relativistic Mechanics :
Minkowski’s space-time diagram, light cone, Four vectors, Lorentz transformation
of Four vectors, Some tensor relations useful in special relativity, Minkowski’s force. (6L)
Ref.1;Ref.2; Ref.3; Ref.6.
8. Covariant formulation of electrodynamics:
Four vector potential, Electromagnetic field tensor, Lorentz force on a charged particle. (4L)
Ref.1, Ref.2, Ref.3, Ref.6.
Text Book :
1. Introduction to Electrodynamics, (3rd Edition) by David J.Griffith.
Publication :Prentice-Hall of India, New Delhi
Reference Books :
2. Introduction to Electrodynamics, by A.Z.Capri and P.V.Panat Narosa Publishing House
3.Classical electricity & Magnetism, by panofsky and Phillips, Addison Wesley
4.Foundations of Electromagnetic theory, by Reitz & Milford, World student series Edition.
5.Classical Electrodynamics, by J.D.Jackson, 3rd Edition John Wiley.
6.Electromagnetic theory and Electrodynamics, by Satya Prakash, Kedar Nath and co.Meerut.
7. Special theory of Relativity, by Robert Resnick.
8. Electromagnetics by B.B.Laud, Willey Eastern.
9. Matrices and Tensors in Physics, A. W. Joshi, 3rd Edition, New Age International
Revised Syllabus
PHYUT602 ATOMS, MOLECULES AND SOLIDS
1. Atoms
Terms for equivalent & non-equivalent electron atom, Hyperfine structure, Width of
spectral line, Nuclear spin, Normal & anamolous Zeeman effect, Paschen – Back effect.
Ref.1: – Ch-2. (5L +2P)
2. Molecules
Rotational & Vibrational spectra for diatomic molecules, Electronic spectra of diatomic
Molecule, Vibrational coarse structure, Vibrational analysis of band system, Frank-Condon
principle, Dissociation energy & dissociation products, Rotational fine structure of
electronic vibration transitions, Electronic angular momentum in diatomic molecule.
Ref.3: Ch.6; Ref.2: Ch 9.1-9.11 (9L+2P)
NMR Spectroscopy: Nuclear spin magnetic moment, Interaction of nuclear magnet with
external magnetic field, NMR spectrometer, chemical shift, Applications.
Ref.3: Ch-7.2 – 7.2.1 (3L)
ESR Spectroscopy: Electron spin interaction with external magnetic field, Simple ESR
Spectrometer, ESR spectrum, Applications.
Ref.2: Ch.11.1 – 11.3 (3L)
3. Soilds
Laue theory of X-ray diffraction, Geometrical structure factor, Atomic scattering
factor, calculations for bcc, fcc & diamond structure. (2L +3P)
Ref. 6: ch-2
Imperfections in crystals: Lattice defects & configurational entropy, vacancies, Schottky
& Frankel pairs, Edge & screw dislocations (qualitative ideas), Experimental methods to
observe defects.
Ref.6: ch.2 and Ref.4 :ch.3,4 (5L+2P)
4. Lattice vibrations and specific heat of solids:
Brillouin zone, Phonon, Vibrational modes of monoatomic linear lattice & diatomic lattice,
Acoustic & optical modes of vibration, lattice heat capacity, Einstein & Debye model of lattice heat
capacity, Normal & Umklappy processes.
Ref. 6: ch. 4,5 and Ref.4: ch.2 (10L+2P)
Reference books :
1. Atomic spectra & atomic structure, Gerhard Hertzberg : Dover publication, New york
Recent edition.
2. Molecular structure & spectroscopy, G.Aruldhas; Prentice – Hall of India, New Delhi(2001)
3. Fundamentals of molecular spectroscopy, Colin N.Banwell & Elaine M.McCash, Tata
McGraw –Hill publishing company limited, Fourth edition(2002).
4. Solid State Physics, A.J.Dekker, Macmillan India Ltd. (2005)
5. Quantum Physics of atoms, molecules, solids nuclei & particles, Robert Eisberg, Robert
Resnick, Second edition, John Wiely & sons(Asia) Ltd.(1985)
6. Solid State Physics, Charles Kittel , John Willey & sons
7. Material Science & Engineering, V.Raghavan, Prentice –Hall of India, New Delhi (2001)
Revised Syllabus
PHYUT603 STATISTICAL MECHANICS
1.Statistical Description of System of Particles :
Specification of the state of the system, Macroscopic and Microscopic states, Phase space,
Statistical ensemble, Postulate of equal a priori probability, Probability calculations, Behaviour
of density of states, Liouville’s theorem(Classical), Quasi-static processes. (4L+1P)
2. Statistical Thermodynamics :
Equilibrium conditions and constraints, Distribution of energy between systems in equilibrium,
Approach to thermal equilibrium, Temperature, Heat reservoir, Sharpness of the probability
distribution, Dependence of the density of states on the external parameters, Equilibrium
between interacting systems. (5L+1P)
3. Classical Statistical Mechanics :
Micro-canonical ensemble, System in contact with heat reservoir, Canonical
ensemble, Applications of canonical ensembles ( Paramagnetism, Molecule in an ideal gas,
Law of atmosphere), System with specified mean energy, Calculation of mean values and
fluctuations in a canonical ensemble, Connection with thermodynamics, Grand-canonical
ensemble, Physical interpretation of , Chemical potential in the equilibrium state, Mean
values and fluctuations in grand canonical ensemble, Thermodynamic functions in terms of
the Grand partition function. (6L+2P)
4.Applications of Statistical Mechanics:
Classical partition functions and their properties, Calculations of thermodynamic
quantities, Ideal monoatomic gas, Gibbs paradox, Equipartition theorem and its Simple
applications. i) Mean kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas ii) Brownian motion iii) Harmonic
Oscillator iv) Specific heat of solid.
Maxwell velocity distribution , Related distributions and mean values. (6L +1P)
5. Quantum Statistics of Ideal Gases :
Symmetry of wave functions, Quantum distribution functions, Boltzmann limit of
Boson and Fermion gases, Evaluation of the partition function, Partition function for diatomic
molecules, Equation of state for an ideal gas, The quantum mechanical paramagnetic
susceptibility. (5L+1P)
6. Ideal Bose System :
Photon gas – i) Radiation pressure ii) Radiation density iii) Emissivity iv) Equilibrium
number of photons in the cavity. Einstein derivation of planck’s law, Bose-Einstein
Condensation, Specific heat, Photon gas – Einstein and Debye’s model of solids. (7L+1P)
7. Ideal Fermi System :
Fermi energy, Mean energy of fermions at absolute zero, Fermi energy as a function
of temperature , Electronic specific heat, White – Dwarfs, Compressibility of Fermi gas,
Pouli’s paramagnetism, A relativistic degenerate electron gas. (7L +1P)
Reference Books :
1. Fundamentals of Statistical and Thermal Physics, - F.Reif, McGraw – Hill, International
Edition (1985)
2. Fundamentals of Statistical Mechanics, B.B.Laud, New Age International Publication (2003)
3. Statistical Mechanics, R.K.Pathria, Bufferworgh Heinemann(2nd Edition)
4. Statistical Mechanics,K.Huang, John Willey & Sons (2nd Edition)
5. Statistical Mechanics,Satya Prakash, Kedar Nath Ram Nath Publication (2008)
6. Statistical Mechanics by Loknathan and Gambhir.
Revised Syllabus
PHYUT 604 QUANTUM MECHANICS – II
1.Approximation Methods :
i) Time-independent Perturbation theory: Non degenerate and degenerate cases (upto
second order). Applications: Zeeman effect, Stark effect, anharmonic oscillator.
ii) Time-dependent Perturbation theory: Transition amplitude 1st and 2nd order, selection
rules, constant perturbation(1st order). Fermi’s golden rule, Harmonic perturbation,
Interaction of atom with em radiation, dipole approx. Einstein coefficient for spontaneous
emission.
iii)Variational method: Basic principles and applications to particle in box, SHO, hydrogen
atom, helium atom.(qualitative approach.)
iv) WKB approximation : Qualitative development and condition for validity of this approx.,
Bohr’s quantization condition, applications to tunnelling such as -particle, field emission.
Ref.1 : chapters 5,9 (16L+8P)
M &W
2. Theory of Scattering :
i) Kinematics: Differential and total cross sections, scattering amplitudes using Green’s function
scattering by symmetric potential, mutual scattering of two particles, Centre of Mass frame,
Laboratory frame.
ii) Dynamics – a) Born approximation, Validity of Born Approx., Application to square
well potential and Yukawa potential.
b) Partial wave analysis, phase shift, scattering amplitudes in terms of phase shift, optical
theorem, scattering by square well potential and perfectly rigid sphere.
Ref.1: Chapter 6 (6.1 to6.5)(6.8 to 6.11)(6.14 to 6.15)(6.17,6.18) (10L +6P)
3. Symmetry in Quantum Mechanics :
Symmetry Parity, Identical particles, symmetric and antisymmetric wave functions,
Slater determinant, collison of identical particles, spin functions for system with more than
one electron. (5L+3P)
Ref.1 Chapter 9, Chapter 6(6.19), Chapter 7 (7.13)
Reference Books :
1.A Text book of Quantum Mechanics, P.M.Mathews and K.Venkatesan, Tata McGraw Hill
2.Quantum Mechanics by A.Ghatak and S.Lokanathan, Macmillan India Ltd.
3.Quantum Mechanics by L.I.Schiff, McGraw Hill
4.Modern Quantum Mechanics by J.J.Sakurai
5.Quantum Physics by R.Eisberg and R.Resnick(Wiley and Sons)
6.Introduction to quantum mechanics by D.I.Griffiths (Pearson Education)(IInd Edition)
PHY UP 505 Basic Physics Laboratory – I
(Any 10 Experiment)
1. Michelson Interferometer.
2. Resistivity of Ge at various temperature by Four Probe method and determination of
band gap.
3. Susceptibility, Gauy method.
4. Ionic Conductivity of NaCl.
5. Skin depth in Al using electromagnetic radiation.
6. Counting statistics, G.M. tube.
7. End point energy and Absorption coefficient using G.M.tube.
8. Conductivity of Plasma at various pressure for AC/DC source.
9. Electron Spin Resonance. (ESR)
10. Fabry-Parot Etalon.
11. Electron Diffraction.
12. Thermionic Emission.
13. Franck – Hertz Experiment.
14. Zeeman Effect.
15. ‘e’ by Millikan oil drop method.
16. Stefan’s constant – Black body radiation.
17. Clausius – Mossotti equation using sugar solution ( Determination of Polarisation.)
18. To study absorption spectra of Iodine molecule and to determine its dissociation energy
using spectrometer.
19. Comparison of resolving limit of optical instruments with human eye.( Pg. 300-301,
A world view of Physics by Prof. D.P. Khandelwal et al. South Asian Publishers pvt. Ltd.
New Delhi, 1999)
20. Study of electromagnetic damping ( Pg. 320, A world view of Physics by Prof. D.P.
Khandelwal et al. South Asian Publishers pvt. Ltd.New Delhi, 1999)
Reference Books :
1. Solid State Laboratory Manual in Physics, Department of Physics, University of Pune,
Pune-7. (1977)
2. Experimental Physics, Wersnop and Flint.
3. Molecular structure and Spectroscopy, G.Aruldas Prentice-hall of India Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi.
4. Solid State Physics, S.P. Pillai (3rd Edition), New age International Publisher.
5. Practical Physics, D.R. Behekar, Dr.S. T. Seman, V.M.Gokhale,P.G.Kale
( Kitab Mahal Publication)
6. Introduction to experimental Nuclear Physics, R.M. Singru, Wiley Eastern private Ltd.
New Delhi.
PHY UP 605 Electronics Laboratory
(Any 10 Experiment)
1. Study of voltage controlled oscillator using IC-566.
2. Frequency multiplier using PLL-565(for 2 & 3 operation using counter.)
3. Fold back power supply.
4. Precision rectifier.
5. Crystal oscillator- Millar type and Digital clock.
6. Diode pump using UJT.
7. DAC (R-2R and Binary type for 4-bit).
8. Pulse train generator.
9. SMPS power supply.
10. CVCC power supply.
11. Active filter- Low pass, High pass, Band pass, and Notch Filter using OP-AMP.
12. Function generator using OP-AMP/IC –8038.
13. Study of optocoupler, MCT2E and their application.
14. Constant current source using OP-AMP.
15. Class-B push pull amplifier using Dual power supply and OP-AMP.
16. Design, built and test oscillator – Wien Bridge oscillator / phase shift oscillator using
OP-AMP.
17.Inductive simulation using OP-AMP.
18. tudy of multiplexer and Demultiplexer.
19. Voltage to Frequency / Frequency to voltage converter using OP-AMP.
20. Study of errors in electrical measurement and results due to loading.
21. Fourier analysis (Pg. 18, Experiments in Electronics, S.V. Subramaniam, McMillan India
Limited, 1982)
22. To determine the transition capacitance of a varactor diode and use it as a variable
capacitor.(Pg. 28, Experiments in Electronics, S.V. Subramaniam, Mcmillan India
Limited, 1982)
23. Measurement of efficiency of a power amplifier.(IC 810)and study of its frequency
response.(Pg. 118, Experiments in Electronics, S.V. Subramaniam, Mcmillan India
Limited, 1982)
24.Study of noise performance of an amplifier.(Pg. 449, Art of Electronics, Horowitz and Hill,
Cambridge, University Press, Low Price Edition, 1995.)
Reference Books :
1.Signetic manual.
2. Power supplied, B.S.Sonde.
3. Digital Principles, Malvino ( 6th Edition, Tata McGraw Hill Publication Co. Ltd. Delhi.)
4. Operational Amplifier , G.B.Clayton.
5. OP-AMPS and Linear integrated circuits, Ramakant Gaikwad.
6.Data Converters, B.S. Sonde, Tata Mc-Graw Hill Pub. Co. Ltd. (1974).
7. Pulse, Digital and Switching Circuits, Miliman & Taub.
8. Electronic Integrated Circuits and Systems, Franklin, C. Fitchen( Van No strand
Reinhold Company).
9. Digital Principles and applications, Leach and Malvino, Tata Mc-Graw Hill Pub.Co.
Ltd. N.Delhi(5th Edition,2002).
|