|
#2
25th September 2014, 10:12 AM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Mahadiscom Exam Syllabus For Electrical Sub Engineer
Here I am providing the Maharashtra State Electricity Distribution Company Limited syllabus for professional examination for Electrical Sub Engineer, the exam is divided into following sections: Transmission of Electricity. National Electricity Policy and Plan. Tariff. Generation of Electricity. Central Electricity Authority. Regulatory Commission. Elements of Double Entry. Rules of Journalising. Ledger Accounts. Sub Divisions of Journal. Cash Book. Appellate Tribunal for Electricity. Reorganisation of Board. Miscellaneous. Banking Transactions. Dishonor of bills payable, retiring bills payable under Discount Foreign and documentary bills. Bill Transactions-Acceptance of Bills, dishonor of bills, Notice and protesting, Discounting Bills, renewal of Bills, Bills payable Accounts. 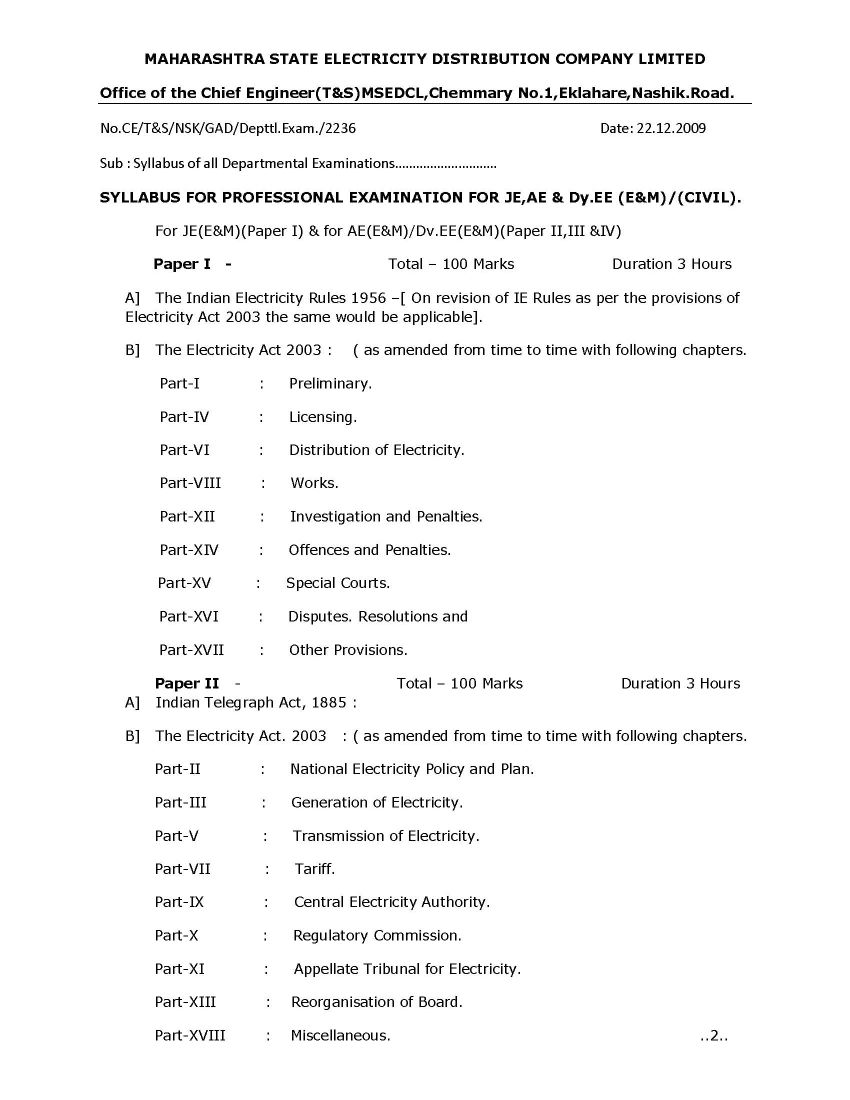     For detailed information , here is the attachment |