As you are asking for ISC Board Physics Practical Question Paper for Class 12 so on your demand I am providing same :
Question 1 [9]
This experiment is based on the principle of a potentiometer.
You are provided with:
(a) a 100 cm long and uniform metallic wire AB fitted on a wooden board across a meter
scale and provided with binding terminals at each end.
(b) a resistance box R having a range of 1Ω to (at least) 10 Ω.
(c) a 2V dc source (an accumulator or an electronic battery). It is labelled as D.
(d) a freshly dry cell. It is kept either in a battery holder or a battery box. It is labelled as
E.
(e) a central zero galvanometer G.
(f) a plug key K.
(g) a jockey J and a few connecting wires.
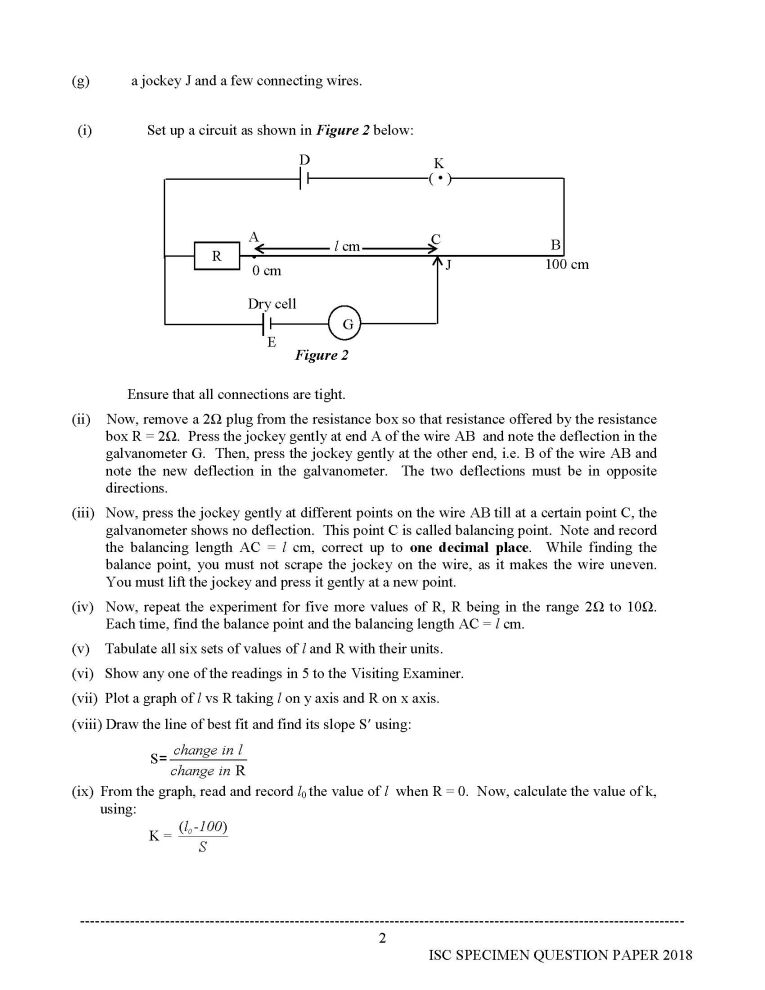
(i) Set up a circuit as shown in Figure 2 below:
(ii) Now, remove a 2Ω plug from the resistance box so that resistance offered by the resistance
box R = 2Ω. Press the jockey gently at end A of the wire AB and note the deflection in the
galvanometer G. Then, press the jockey gently at the other end, i.e. B of the wire AB and
note the new deflection in the galvanometer. The two deflections must be in opposite
directions.
(iii) Now, press the jockey gently at different points on the wire AB till at a certain point C, the
galvanometer shows no deflection. This point C is called balancing point. Note and record
the balancing length AC = l cm, correct up to one decimal place. While finding the
balance point, you must not scrape the jockey on the wire, as it makes the wire uneven.
You must lift the jockey and press it gently at a new point.
(iv) Now, repeat the experiment for five more values of R, R being in the range 2Ω to 10Ω.
Each time, find the balance point and the balancing length AC = l cm.
(v) Tabulate all six sets of values of l and R with their units.
(vi) Show any one of the readings in 5 to the Visiting Examiner.
(vii) Plot a graph of l vs R taking l on y axis and R on x axis.
(viii) Draw the line of best fit and find its slope S using:
S=
R
change in l
change in
(ix) From the graph, read and record l0 the value of l when R = 0. Now, calculate the value of k,
using:
K =
( )
Question 2 [6]
This experiment determines the focal length of the given convex lens by no parallax method.
You are provided with:
(a) A lens holder
(b) A convex lens
(c) Two optical pins
(d) An optical bench
Note: The experiment may be performed on a table top, using a metre scale, in case an optical
bench is not available.
(i) Mount the given convex lens (L) on the lens holder. Adjust the heights of object pin (O)
and image pin (I) till their tips lie on the principal axis of the lens.
(ii)
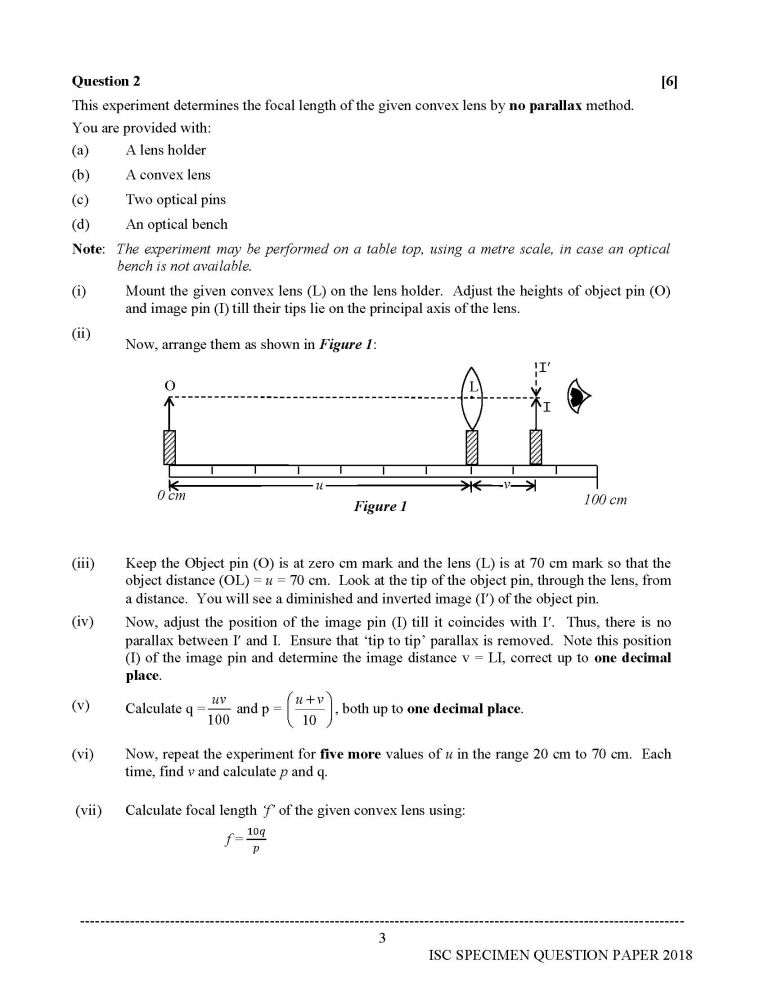
Now, arrange them as shown in Figure 1:
(iii) Keep the Object pin (O) is at zero cm mark and the lens (L) is at 70 cm mark so that the
object distance (OL) = u = 70 cm. Look at the tip of the object pin, through the lens, from
a distance. You will see a diminished and inverted image (I) of the object pin.
(iv) Now, adjust the position of the image pin (I) till it coincides with I. Thus, there is no
parallax between I and I. Ensure that tip to tip parallax is removed. Note this position
(I) of the image pin and determine the image distance v = LI, correct up to one decimal
place.
(v) Calculate q =
100
uv
and p =
10
u v
, both up to one decimal place.
(vi) Now, repeat the experiment for five more values of u in the range 20 cm to 70 cm. Each
time, find v and calculate p and q.
(vii) Calculate focal length f of the given convex lens using:
f =
ISC Board Physics Practical Question Paper for Class 12