|
#2
30th March 2016, 03:09 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: The Compound Microscope
A high power or compound magnifying lens accomplishes larger amounts of amplification than a stereo or low power magnifying lens. It is utilized to see littler examples, for example, cell structures which can't be seen at lower levels of amplification. Basically, a compound magnifying lens comprises of auxiliary and optical segments. In any case, inside of these two fundamental frameworks, there are some key parts that each microscopist ought to know and get it. Compound Microscope Parts A high power or compound magnifying instrument accomplishes more elevated amounts of amplification than a stereo or low power magnifying lens. It is utilized to see littler examples, for example, cell structures which can't be seen at lower levels of amplification. Basically, a compound magnifying lens comprises of basic and optical parts. In any case, inside of these two fundamental frameworks, there are some key segments that each microscopic ought to know and get it. These key magnifying lens parts are represented and clarified underneath. Basic Components The three essential, auxiliary segments of a compound magnifying instrument are the head, base and arm. Head/Body houses the optical parts in the upper part of the magnifying instrument Base of the magnifying instrument bolsters the magnifying lens and houses the illuminator Arm interfaces with the base and backings the magnifying lens head. It is likewise used to convey the magnifying instrument. OPTICAL COMPONENTS There are two optical frameworks in a compound magnifying instrument: Eyepiece Lenses and Objective Lenses: Eyepiece or Ocular is the thing that you look through at the highest point of the magnifying instrument. Regularly, standard eyepieces have an amplifying force of 10x. Discretionary eyepieces of changing forces are accessible, commonly from 5x-30x. Eyepiece Tube holds the eyepieces set up over the goal lens. Binocular magnifying instrument heads commonly join a diopter change ring that takes into consideration the conceivable irregularities of our visual perception in one or both eyes. The monocular (single eye utilization) magnifying lens does not require a diopter. Binocular magnifying instruments additionally swivel (Interpupillary Adjustment) to take into account diverse separations between the eyes of various people. Target Lenses are the essential optical lenses on a magnifying lens. They go from 4x-100x and normally, incorporate, three, four or five on lens on generally magnifying instruments. Destinations can be forward or raise confronting. Nosepiece houses the destinations. The goals are uncovered and are mounted on a pivoting turret so that distinctive targets can be helpfully chosen. Standard targets incorporate 4x, 10x, 40x and 100x albeit diverse force destinations are accessible. Coarse and Fine Focus handles are utilized to center the magnifying lens. Progressively, they are coaxial handles - that is to say they are based on the same hub with the fine center handle all things considered. Coaxial center handles are more helpful since the viewer does not need to grab for an alternate handle. Stage is the place the example to be seen is set. A mechanical stage is utilized when working at higher amplifications where fragile developments of the example slide are required. Stage Clips are utilized when there is no mechanical stage. The viewer is required to move the slide physically to see distinctive segments of the example. Opening is the gap in the stage through which the base (transmitted) light achieves the stage. Illuminator is the light hotspot for a magnifying lens, regularly situated in the base of the magnifying lens. Most light magnifying lens utilize low voltage, halogen knobs with nonstop variable lighting control situated inside of the base. Condenser is utilized to gather and center the light from the illuminator on to the example. It is situated under the stage regularly in conjunction with an iris stomach. Iris Diaphragm controls the measure of light achieving the example. It is situated over the condenser and underneath the stage. Most great magnifying lens incorporate an Abbe condenser with an iris stomach. Joined, they control both the center and amount of light connected to the example. Condenser Focus Knob moves the condenser up or down to control the lighting concentrate on the example. 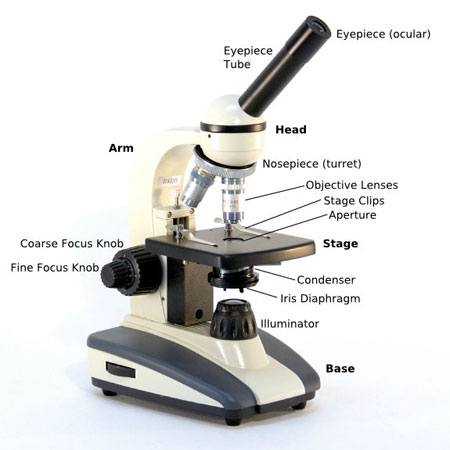 |