|
#2
18th December 2016, 11:20 PM
| |||
| |||
| Quote:
|
|
#1
22nd June 2015, 01:56 PM
| |||
| |||
| Chemistry General Syllabus Of West Bengal State University
Hello Sir I am pursuing B.Sc Chemistry (General) (Part 1) from West Bengal State University (WBSU). My Exam is about to come so I have started its preparation but I want to prepare according to syllabus. Would you provide me syllabus of B.Sc (General) (Part 1) of (WBSU)?
|
|
#2
18th December 2016, 11:20 PM
| |||
| |||
| Quote:
|
|
#3
9th October 2019, 12:24 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Chemistry General Syllabus Of West Bengal State University
here I am looking for Chemistry General Syllabus Of West Bengal State University , so will you plz let me know from where I can do download its syllabus on free of cost ??
|
|
#4
9th October 2019, 12:27 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: Chemistry General Syllabus Of West Bengal State University
As you are asking for West Bengal State University General Chemistry Syllabus , so on your demand I am providing same : SEMESTER-I ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ CEMGCOR01T: ATOMIC STRUCTURE, CHEMICAL PERIODICITY, ACIDS AND BASES,REDOX REACTIONS, GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY & ALIPHATIC HYDROCARBONS (Credits: Theory-04, Practicals-02) Theory: 60 Lectures Marks: 50 Section A: Inorganic Chemistry-I (30 Lectures) Marks: 25 Atomic Structure (10 Lectures) Bohr's theory for hydrogen atom (simple mathematical treatment), atomic spectra of hydrogen and Bohr's model, Sommerfeld's model, quantum numbers and their significance, Pauli's exclusion principle, Hund's rule, electronic configuration of many-electron atoms, Aufbau principle and its limitations. Chemical Periodicity (05 Lectures) Classification of elements on the basis of electronic configuration: general characteristics of s-, p-, d- and f-block elements. Positions of hydrogen and noble gases. Atomic and ionic radii, ionization potential, electron affinity, and electronegativity; periodic and group-wise variation of above properties in respect of s- and p- block elements. Acids and bases (10 Lectures) BronstedLowry concept, conjugate acids and bases, relative strengths of acids and bases, effects of substituent and solvent, differentiating and levelling solvents. Lewis acid-base concept, classification of Lewis acids and bases, Lux-Flood concept and solvent system concept. Hard and soft acids and bases ( HSAB concept), applications of HSAB process. Redox reactions (05 Lectures) Balancing of equations by oxidation number and ion-electron method oxidimetry and reductimetry. Section B: Organic Chemistry-I (30 Lectures) Marks: 25 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry (5 Lectures) Electronic displacements: inductive effect, resonance and hyperconjugation; cleavage of bonds: homolytic and heterolytic; structure of organic molecules on the basis of VBT; nucleophiles electrophiles; reactive intermediates: carbocations, carbanions and free radicals. 7 Stereochemistry (8 Lectures) Different types of isomerism; geometrical and optical isomerism; concept of chirality and optical activity (up to two carbon atoms); asymmetric carbon atom; elements of symmetry (plane and centre); interconversion of Fischer and Newman representations; enantiomerism and diastereomerism, meso compounds; threo and erythro, D and L, cis and trans nomenclature; CIP Rules: R/S (upto 2 chiral carbon atoms) and E/Z nomenclature. Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination Reactions (5 Lectures) Nucleophilic substitutions: SN1 and SN2 reactions; eliminations: E1 and E2 reactions (elementary mechanistic aspects); Saytzeff and Hofmann eliminations;elimination vs substitution. Aliphatic Hydrocarbons (12 Lectures) Functional group approach for the following reactions (preparations & reactions) to be studied in context to their structures. Alkanes  up to 5 Carbons). Preparation: catalytic hydrogenation, Wurtz reaction, Kolbes up to 5 Carbons). Preparation: catalytic hydrogenation, Wurtz reaction, Kolbessynthesis, from Grignard reagent. Reactions: mechanism forfree radical substitution: halogenation. Alkenes  up to 5 Carbons). Preparation: elimination reactions: dehydration of alcohols and up to 5 Carbons). Preparation: elimination reactions: dehydration of alcohols anddehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides; cis alkenes (partial catalytic hydrogenation) and trans alkenes (Birch reduction). Reactions: cis-addition (alkaline KMnO4) and trans-addition (bromine) with mechanism, addition of HX [Markownikoffs (with mechanism) and antiMarkownikoffs addition], hydration, ozonolysis, oxymercuration-demercuration and hydroboration-oxidation reaction. Alkynes: (up to 5 Carbons). Preparation: acetylene from CaC2 and conversion into higher alkynes; by dehalogenation of tetra halides and dehydrohalogenation of vicinal dihalides. Reactions: formation of metal acetylides, addition of bromine and alkaline KMnO4, ozonolysis and oxidation with hot alkaline KMnO4 West Bengal State University General Chemistry Syllabus  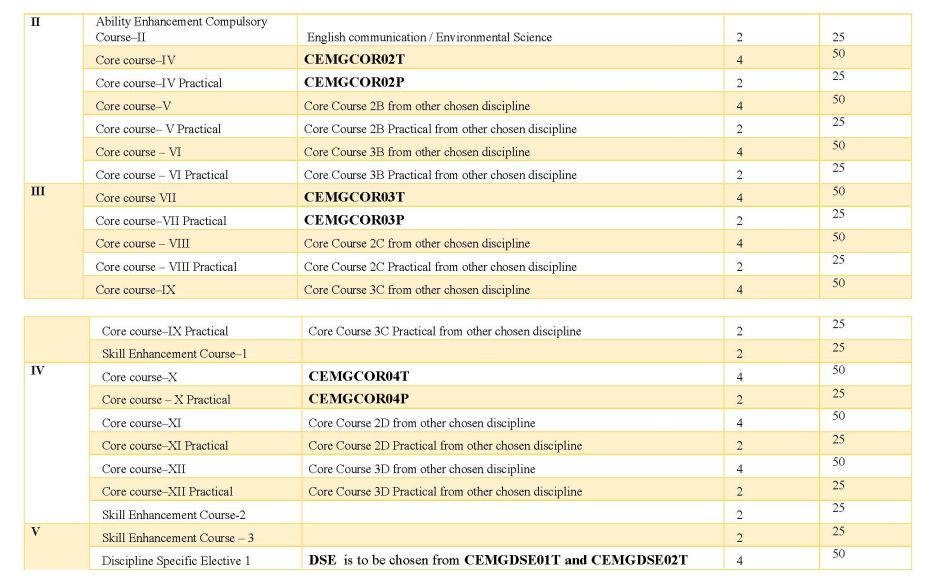   |
| Thread Tools | Search this Thread |
| |