|
#4
21st May 2015, 04:34 PM
| |||
| |||
| Re: CBSE Economics Syllabus
The CBSE or Central Board of Secondary Education Economics class 12th syllabus as you will be giving the exam this year is as follows: Part A: Introductory Microeconomics Unit 1: Introduction 11 Periods Meaning of microeconomics and macroeconomics What is an economy? Central problems of an economy: what, how and for whom to produce; concepts of production possibility frontier and opportunity cost. Unit 2: Consumer's Equilibrium and Demand 34 Periods Consumer's equilibrium - meaning of utility, marginal utility, law of diminishing marginal utility, conditions of consumer's equilibrium using marginal utility analysis. Indifference curve analysis of consumer's equilibrium-the consumer's budget (budget set and budget line), preferences of the consumer (indifference curve, indifference map) and conditions of consumer's equilibrium. Demand, market demand, determinants of demand, demand schedule, demand curve, movement along and shifts in the demand curve; price elasticity of demand - factors affecting price elasticity of demand; measurement of price elasticity of demand - (a) percentage-change method and (b) geometric method (linear demand curve); relationship between price elasticity of demand and total expenditure. Unit 3: Producer Behaviour and Supply 34 Periods Production function: Total Product, Average Product and Marginal Product. Returns to a Factor. Cost and Revenue: Short run costs - total cost, total fixed cost, total variable cost; Average fixed cost, average variable cost and marginal cost-meaning and their relationship. Revenue - total, average and marginal revenue. Producer's equilibrium-meaning and its conditions in terms of marginal revenue-marginal cost. Supply, market supply, determinants of supply, supply schedule, supply curve, movements along and shifts in supply curve, price elasticity of supply; measurement of price elasticity of supply - (a) percentage-change method and (b) geometric method. Unit 4: Forms of Market and Price Determination under Perfect Competition with simple applications. 31 Periods Perfect competition - Features; Determination of market equilibrium and effects of shifts in demand and supply. Other Market Forms - monopoly, monopolistic competition, oligopoly - their meaning and features. Simple Applications of Demand and Supply: Price ceiling, price floor. Part B: Introductory Macroeconomics Unit 5: National Income and Related Aggregates 32 Periods Some basic concepts: consumption goods, capital goods, final goods, intermediate goods; stocks and flows; gross investment and depreciation. Circular flow of income; Methods of calculating National Income - Value Added or Product method, Expenditure method, Income method. Aggregates related to National Income: Gross National Product (GNP), Net National Product (NNP), Gross and Net Domestic Product (GDP and NDP) - at market price, at factor cost; National Disposable Income (gross and net), Private Income, Personal Income and Personal Disposable Income; Real and Nominal GDP. GDP and Welfare Unit 6: Money and Banking 18 Periods Money - its meaning and functions. Supply of money - Currency held by the public and net demand deposits held by commercial banks. Money creation by the commercial banking system. Central bank and its functions (example of the Reserve Bank of India): Bank of issue, Govt. Bank, Banker's Bank, Controller of Credit through Bank Rate, CRR, SLR, Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate, Open Market Operations, Margin requirement. Unit 7: Determination of Income and Employment 27 Periods Aggregate demand and its components. Propensity to consume and propensity to save (average and marginal). Short-run equilibrium output; investment multiplier and its mechanism. Meaning of full employment and involuntary unemployment. Problems of excess demand and deficient demand; measures to correct them - change in government spending, availability of credit. Unit 8: Government Budget and the Economy 17 Periods Government budget - meaning, objectives and components. Classification of receipts - revenue receipts and capital receipts; classification of expenditure - revenue expenditure and capital expenditure. Measures of government deficit - revenue deficit, fiscal deficit, primary deficit their meaning. Unit 9: Balance of Payments 16 Periods Balance of payments account - meaning and components; balance of payments deficit-meaning. Foreign exchange rate - meaning of fixed and flexible rates and managed floating. Determination of exchange rate in a free market. CBSE Economics Syllabus    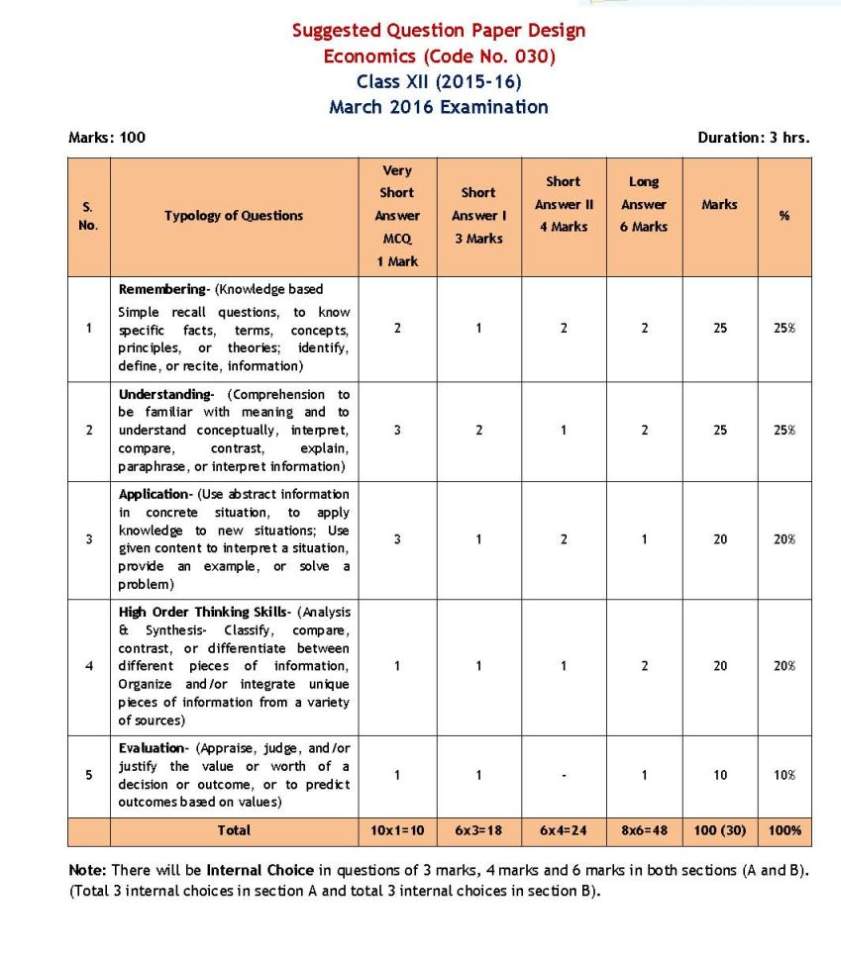 |