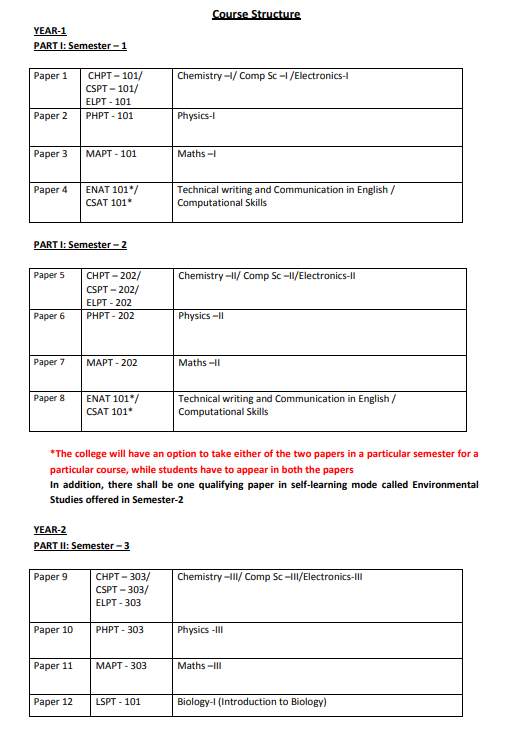
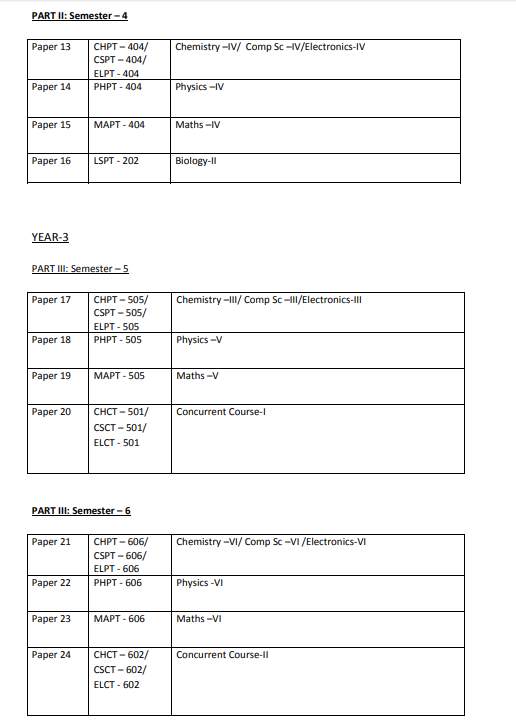
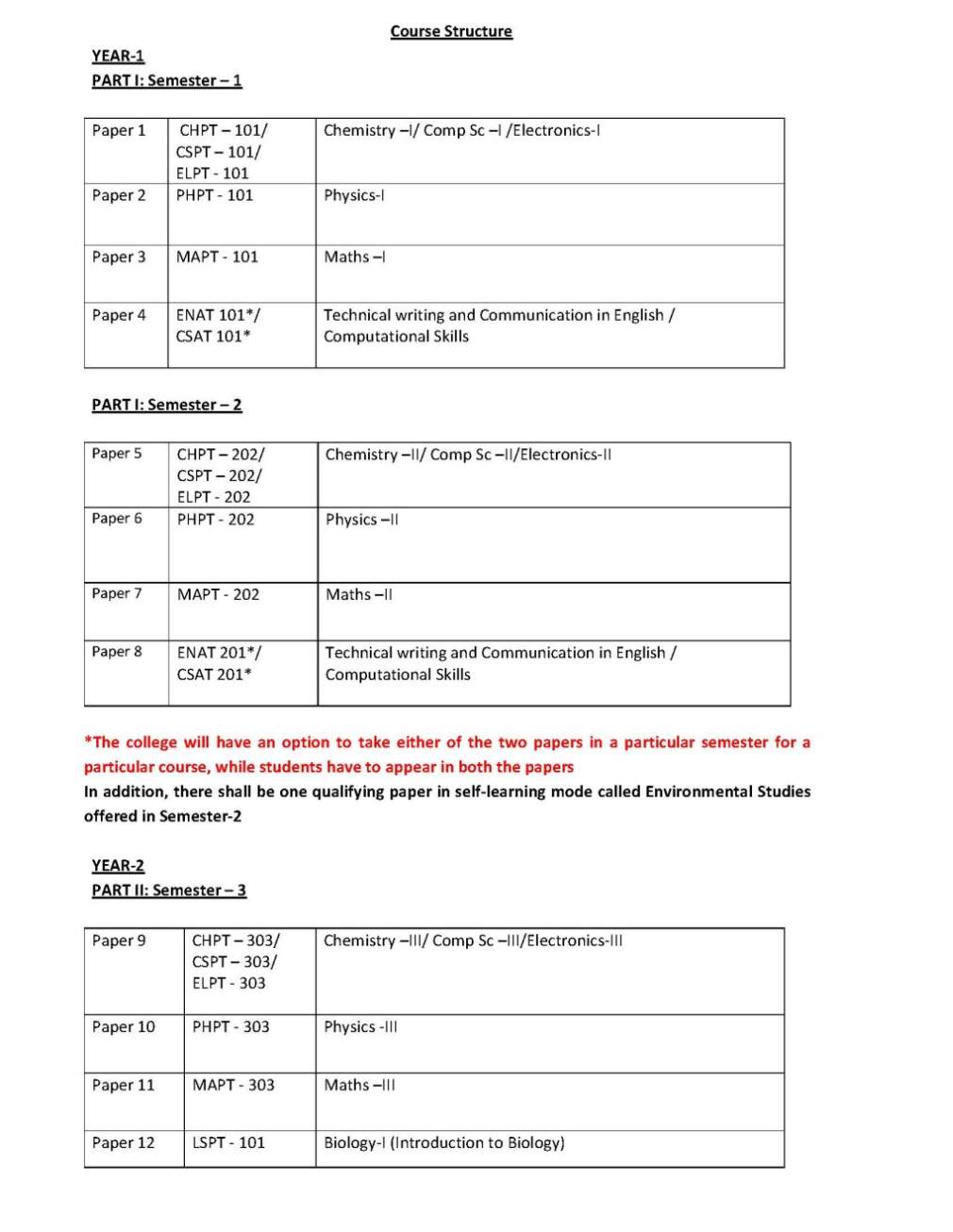
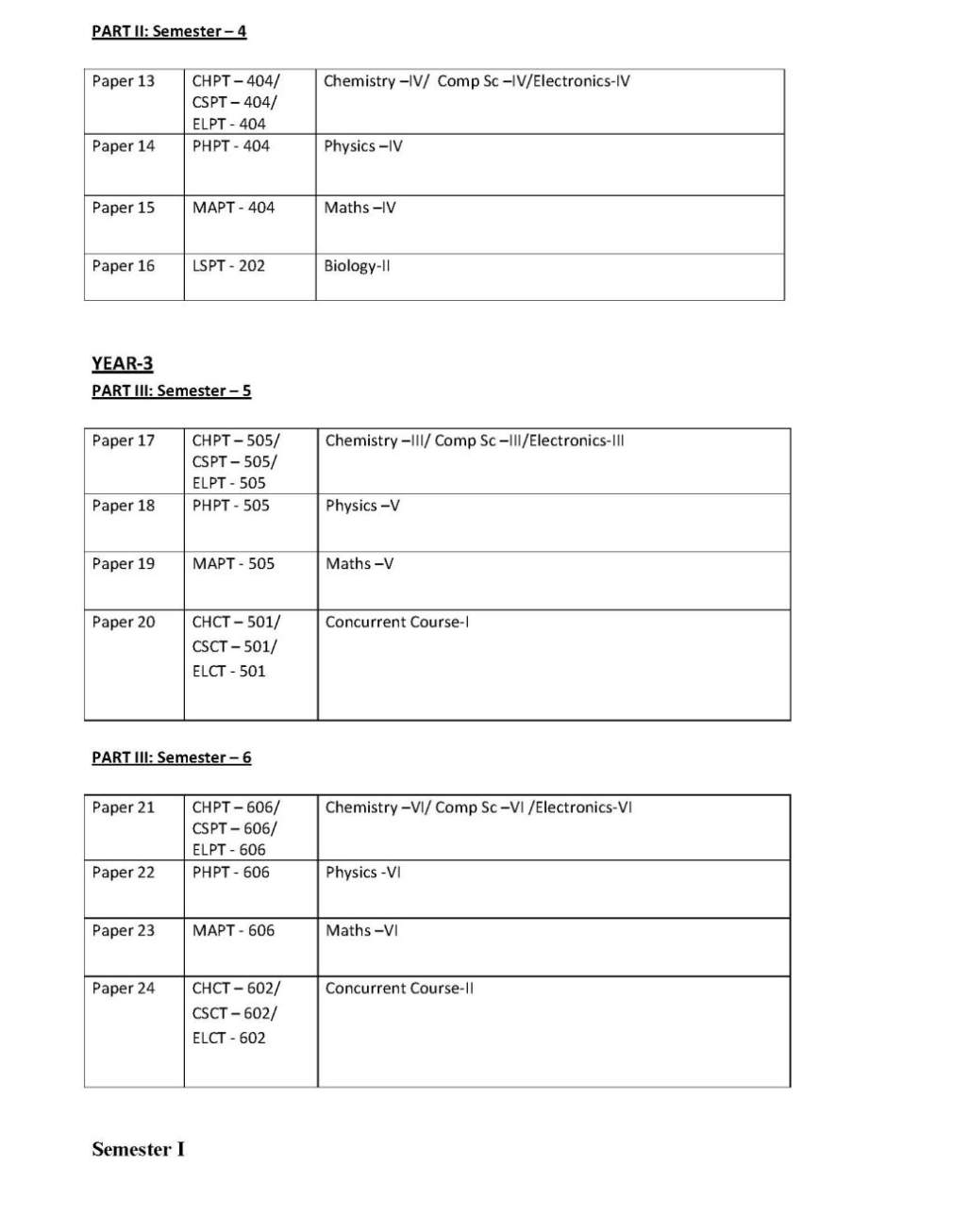
The syllabus of 3year full time B.Sc. (Bachelor of Science) Physical Sciences Program offered by University of Delhi, Delhi is as follows:
Semester I
Paper 1
Chemistry –I/ Comp Sc –I /Electronics-I
CHPT-101: Atomic Structure, Bonding, General Organic Chemistry & Aliphatic
Hydrocarbons
THEORY Marks: 100
Section A: Inorganic Chemistry-1 (30 Lectures)
Unit 1 : Atomic Structure: Recapitulation of: Bohr’s theory de-Broglie’s relation, Heisenberg Uncertainty principle. Need of a new approach to Atomic structure.
Time independent Schrodinger equation (H Ψ = EΨ). Significance of Ψ and Ψ2
, Schrodinger equation for hydrogen atom. Transformation of Cartesian coordinates (x,y,z) into polar coordinates (r,θ,φ). Radial and angular parts of the hydogenic wavefunctions (atomic orbitals) and their variations for 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p and 3d orbitals. (Only graphical representation), Radial and angular nodes and their significance Radial
distribution functions (1s and 2s atomic orbitals). Significance of quantum numbers, orbital angular momentum and quantum numbers mr and ms. Shapes of s, p and d atomic orbitals, nodal planes. Discovery of spin, spin quantum number (s) and magnetic spin quantum number (ms) Electronic configurations of the atoms Concept of exchange energy Relative energies of atomic orbitals, Anomalous electronic configurations
Unit 2: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Ionic Bonding : Energy considerations in ionic bonding, lattice energy and solvation energy and their
importance in the context of stability and solubility of ionic compounds. Born-Lande equation for calculation
of lattice energy, Born-Haber cycle and its applications, polarizing power and polarizability. Fajan’s rules,
bond moment, dipole moment and percentage ionic character.
Covalent bonding :
VB Approach : Concept of hybridization and VSEPR theory .
Resonance and resonance energy : study of some inorganic and organic compounds.
Molecular Orbital Approach : LCAO method, bonding and antibonding MOs and their characteristics for s-s,
s-p and p-p combination of atomic orbitals, non- bonding combination of orbitals ,MO treatment of
homonuclear diatomic molecules of 1st and 2nd periods (including idea of s-p mixing) and heteronuclear
diatomic molecules such as CO, NO and NO+.
Comparison of
VB and MO approaches.
Syllabus B.Sc. Physical Sciences University of Delhi, Delhi